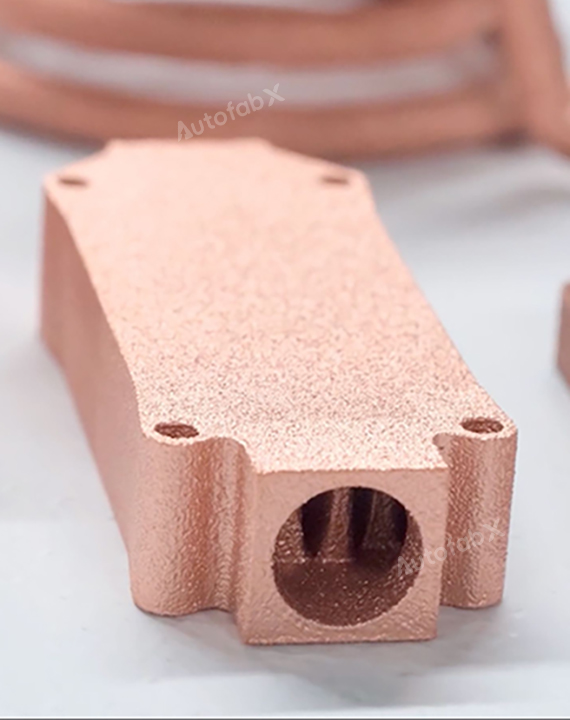
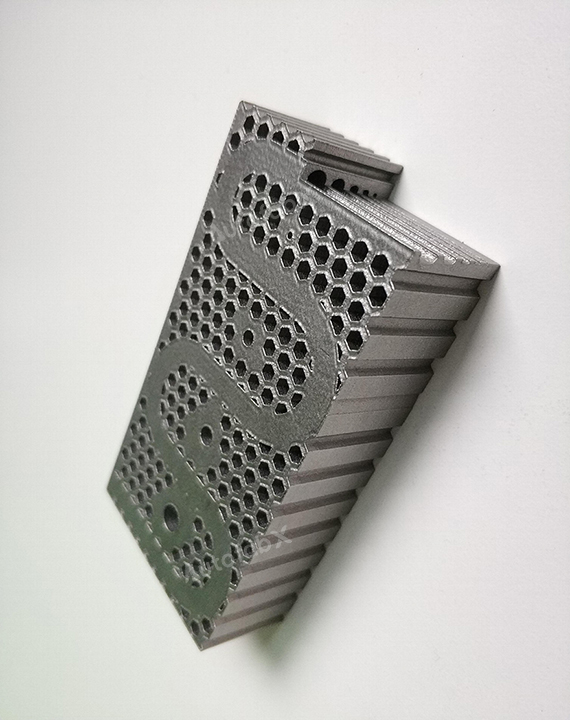
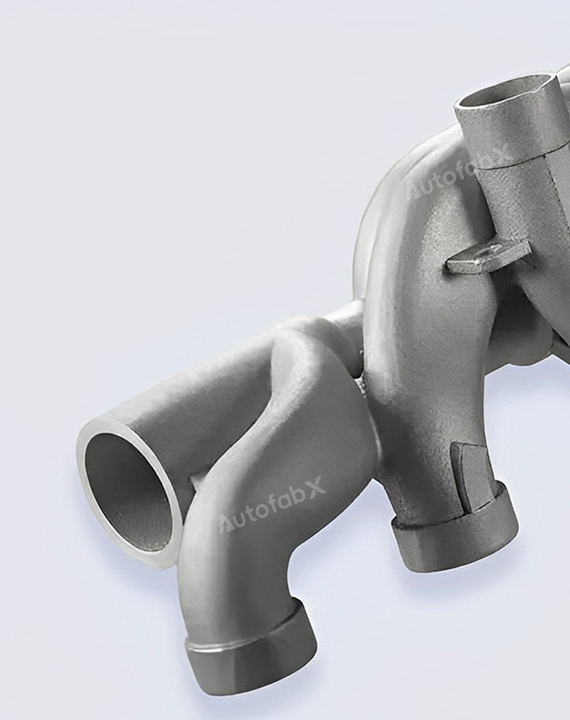
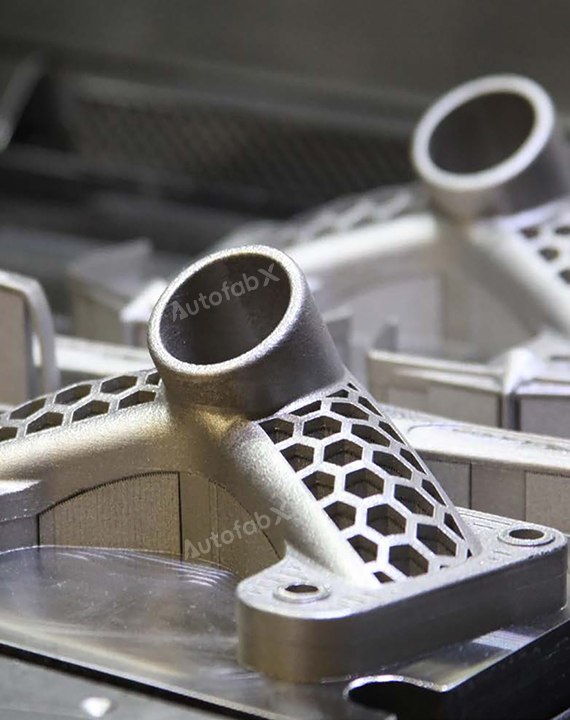
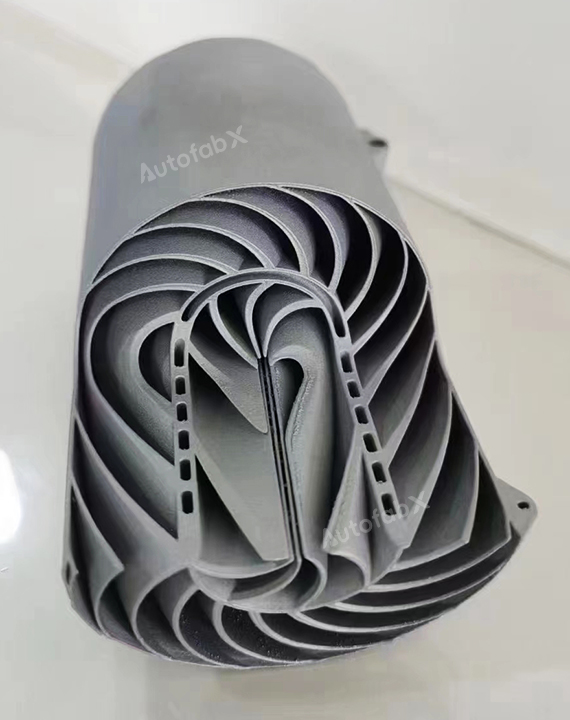
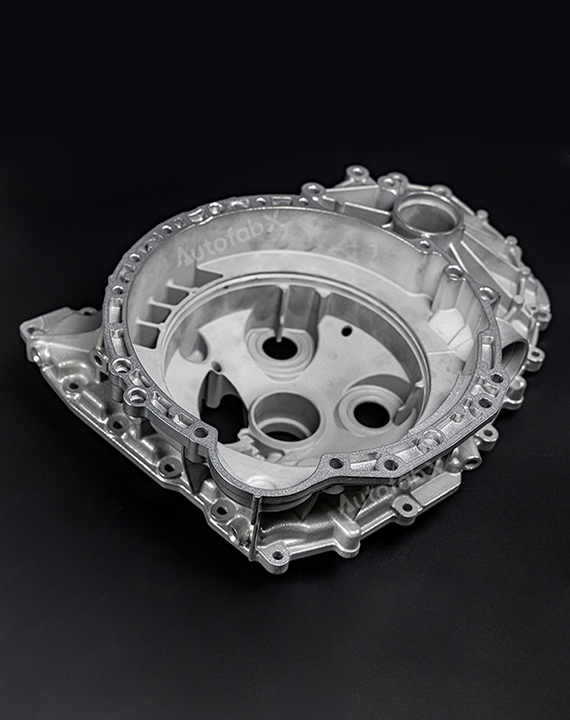
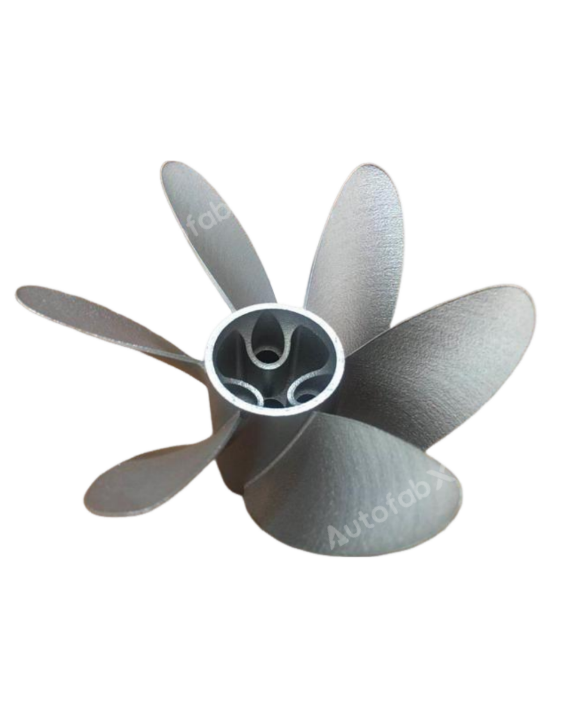
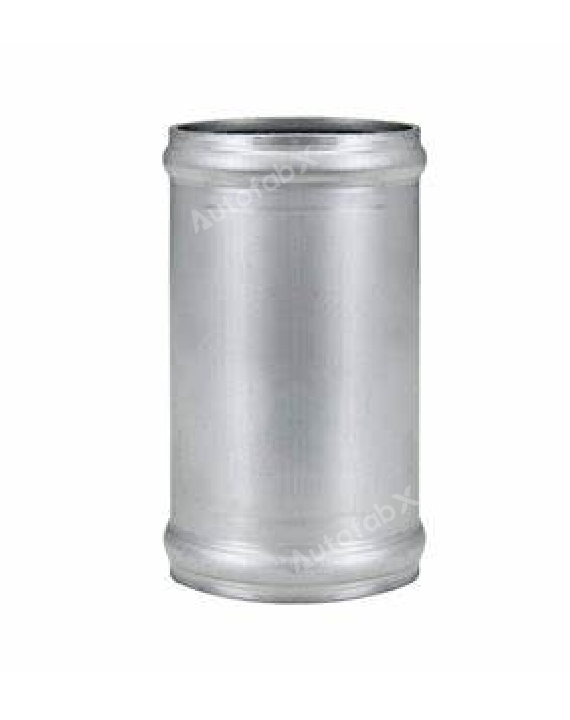
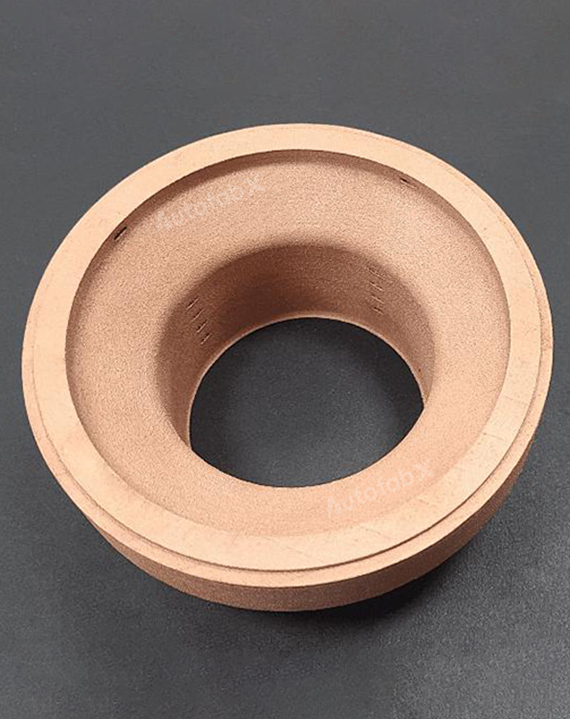
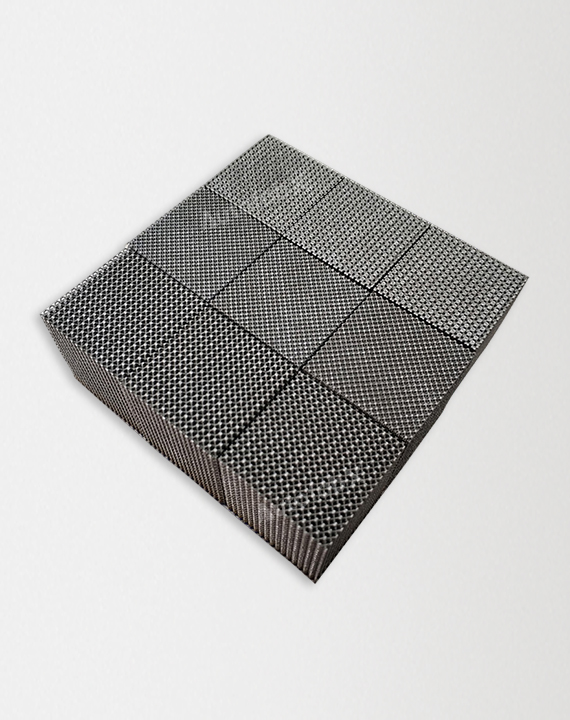
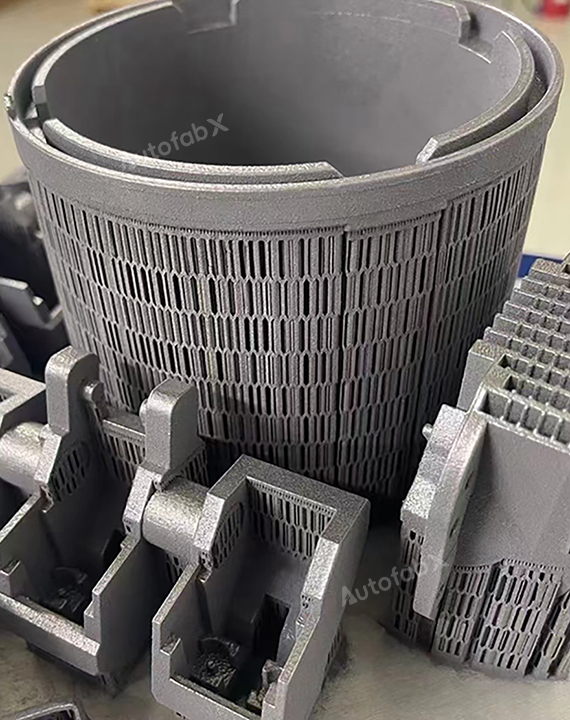
Custom Online Selective Laser Melting(SLM) Services
Quick SLM quotes via AutofabX for rapid metal prototypes and production parts. We are ISO 9001, 13485 and AS9100 certified.
Start A New Quote
STEP | STP | IGS | DWG | DXF | PDF FilesSelective Laser Melting(SLM) Materials
Aluminum(6061)
Aluminum (6061) is a versatile alloy renowned for its balanced blend of strength, corrosion resistance, and formability.
Finishing:
Laser Engraving, Sand Blasting, Shot Peening , Heat Treatment, Polishing, Anodizing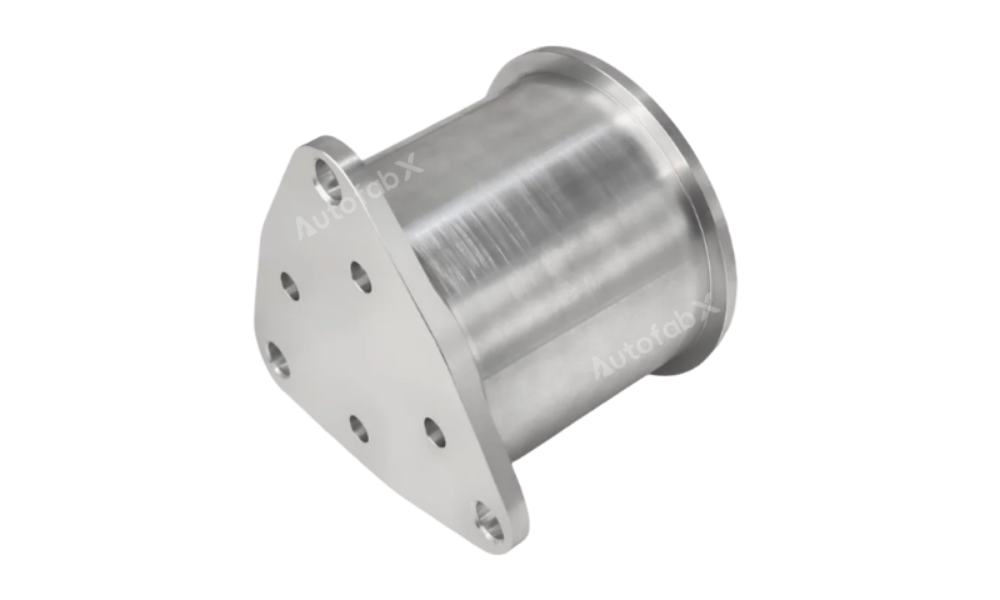
Overview
What is Selective Laser Melting (SLM)?
Selective Laser Melting (SLM) is an additive manufacturing process that uses a high-powered laser to fully melt and fuse metallic powder, layer by layer, to create fully dense, complex metal parts. It is known for its ability to produce high-strength parts with excellent mechanical properties, suitable for both prototyping and end-use production.
Why Choose AutofabX for SLM Services?
AutofabX provides high-quality SLM printing services with several key advantages:
High Strength and Density: Our SLM process produces fully dense metal parts with excellent mechanical properties, making them suitable for demanding applications.
Material Variety: AutofabX offers a wide range of metal powders, including stainless steel, titanium, aluminum, and more, to meet different application needs.
Complex Geometries: SLM allows for the production of complex, lightweight structures that are difficult or impossible to manufacture using traditional methods.
Expert Guidance: Our experienced team provides design optimization for additive manufacturing, ensuring the best possible results for your SLM projects.
How Selective Laser Melting Works
Design: The process begins with a 3D CAD model, which is prepared in slicing software to create a layer-by-layer plan.
Powder Layering: A thin layer of metal powder is spread across the build platform.
Laser Melting: A high-powered laser selectively melts the powder particles by scanning over the surface, following the cross-sectional pattern of the part.
Layering: The build platform lowers, and a new layer of powder is spread. The laser fuses this layer with the previous one, and the process continues until the part is complete.
Cooling and Post-Processing: Once the build is complete, the parts are allowed to cool before excess powder is removed. Post-processing may include heat treatment, machining, or surface finishing.
Main Equipment for SLM Printing and Popular Brands
EOS M 290: Known for its high precision and reliability, widely used for producing industrial-grade metal parts.
Renishaw RenAM 500: Offers excellent quality and productivity, ideal for producing complex metal components for various industries.
Advantages and Limitations of SLM Printing
Advantages:
High Strength and Density: SLM produces parts that are fully dense and have mechanical properties comparable to traditionally manufactured metal parts.
Complex Geometries: SLM allows for the creation of complex geometries and internal features that are difficult or impossible to achieve with conventional manufacturing methods.
Material Flexibility: SLM can work with a variety of metal alloys, providing flexibility for different applications.
High Precision: The process provides high dimensional accuracy, making it suitable for precision components.
Limitations:
Cost: SLM is an expensive process due to the cost of metal powders and the high energy consumption of the laser.
Post-Processing Requirements: Parts often require significant post-processing, such as heat treatment or machining, to achieve the desired properties and surface finish.
Residual Stress: The rapid heating and cooling cycles can introduce residual stresses, which may require heat treatment to relieve.
Industry Applications and Case Studies for SLM Printing
Aerospace Industry:
Application: Production of lightweight, high-strength components for aircraft and spacecraft.
Case Study: An aerospace manufacturer used SLM to produce complex titanium brackets, reducing weight and maintaining the required strength for flight applications.
Medical Industry:
Application: Production of custom implants and surgical instruments.
Case Study: A medical device company utilized SLM to produce patient-specific titanium implants, providing a perfect fit and reducing recovery time.
Automotive Industry:
Application: Manufacturing of lightweight components and prototypes for high-performance vehicles.
Case Study: An automotive company used SLM to create aluminum alloy engine parts, optimizing weight and performance for a racing car.
Quality Control Standards and Inspection Methods for SLM Printing
Dimensional Inspection
Tools: Coordinate Measuring Machines (CMM) and laser scanners are used to verify the dimensions of printed parts.
Density and Porosity Testing
Methods: Density testing is performed to ensure the parts are fully dense, while X-ray or CT scanning is used to detect internal porosity.
Mechanical Property Testing
Methods: Tensile, hardness, and fatigue tests are conducted to ensure that the printed parts meet the required mechanical standards.
SLM Printing Design Guidance Table
| Design Aspect | Recommendation |
| Minimum Wall Thickness | 1.0 mm |
| Minimum Feature Size | 0.5 mm |
| Overhangs | Use support for angles > 45° |
| Tolerance | ±0.1 mm |
| Layer Height | 20-60 microns |
SLM Printing Precision Table
| Printing Process | Typical Tolerance |
| Selective Laser Melting (SLM) | ±0.1 mm |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about SLM Printing
What materials can be used in SLM printing?
SLM can use a variety of metal powders, including stainless steel, aluminum, titanium, and cobalt-chrome, suitable for high-strength applications.
Is SLM printing suitable for functional parts?
Yes, SLM produces fully dense metal parts with excellent mechanical properties, making it ideal for functional and load-bearing applications.
What industries benefit from SLM printing?
Industries such as aerospace, medical, and automotive benefit from the high strength, precision, and design flexibility offered by SLM printing.
How accurate is SLM printing?
SLM printing can achieve tolerances of ±0.1 mm, making it suitable for precision components and detailed designs.
What post-processing is required for SLM-printed parts?
Post-processing may include heat treatment, machining, or surface finishing to improve mechanical properties and achieve the desired surface quality.
Can SLM print complex internal geometries?
Yes, SLM can print complex internal geometries and lattice structures, providing design freedom not possible with traditional manufacturing.
How strong are SLM-printed parts?
SLM-printed parts are fully dense and have mechanical properties comparable to or better than traditionally manufactured metal parts, depending on the material and process parameters.
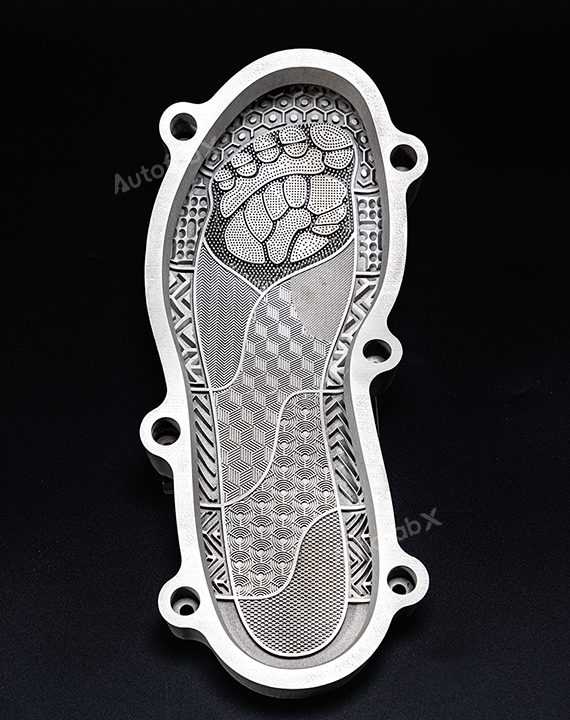
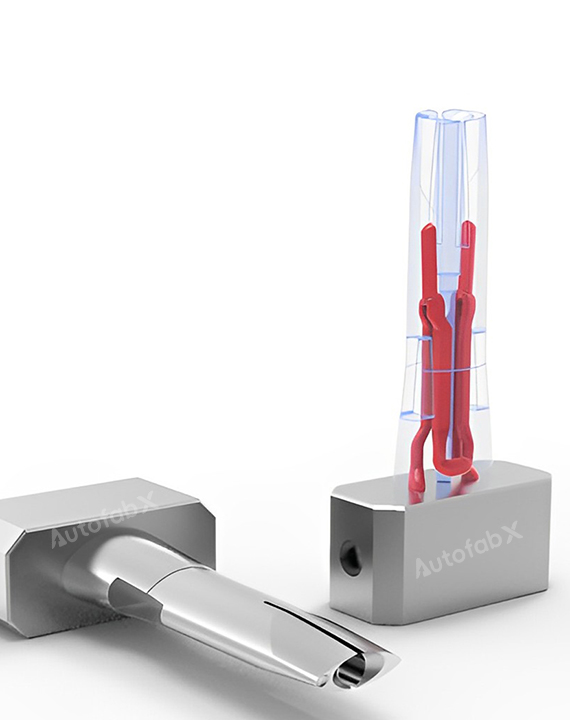
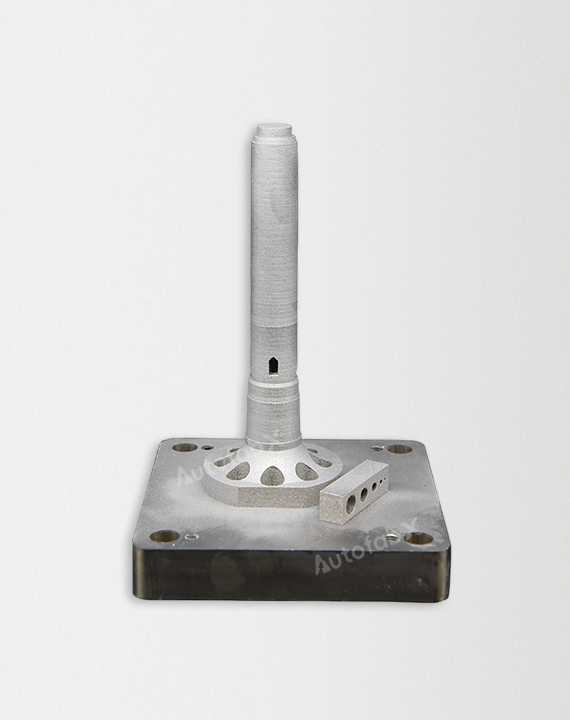
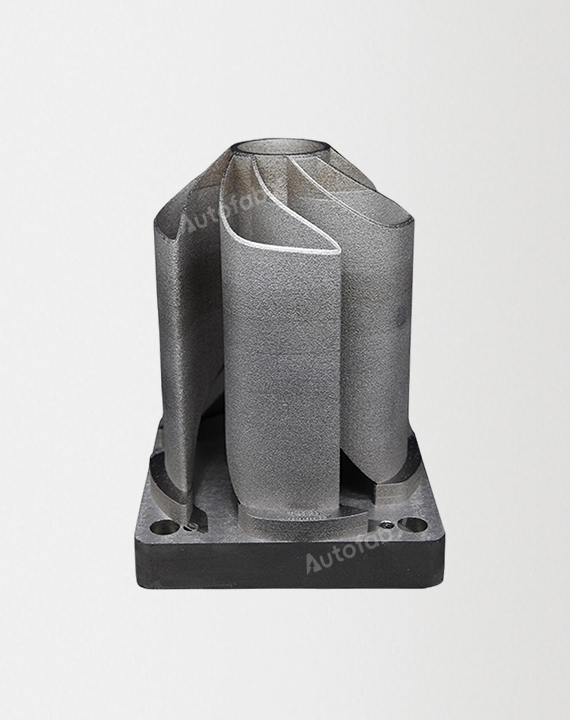
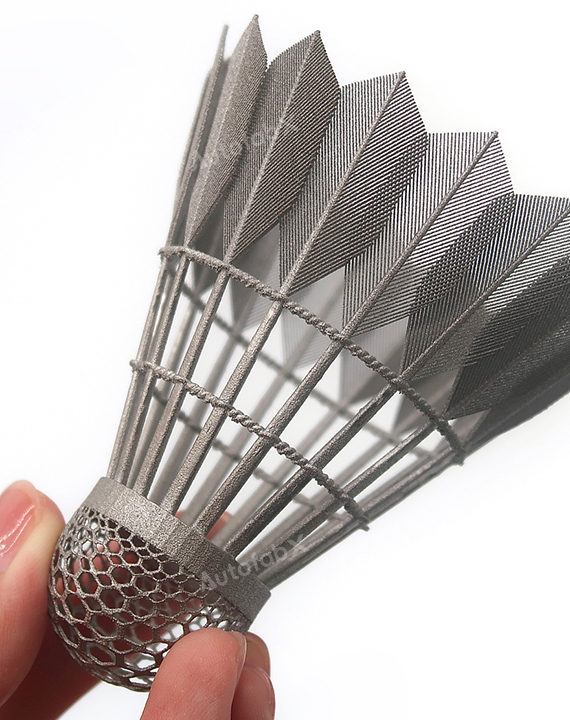
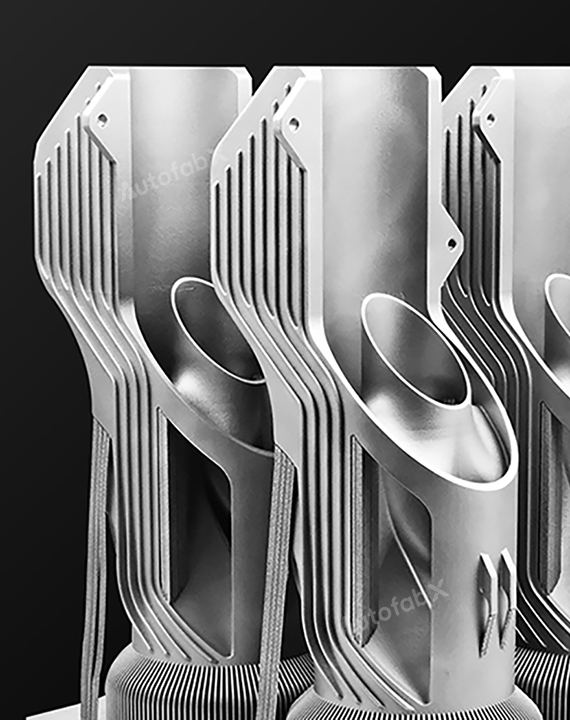
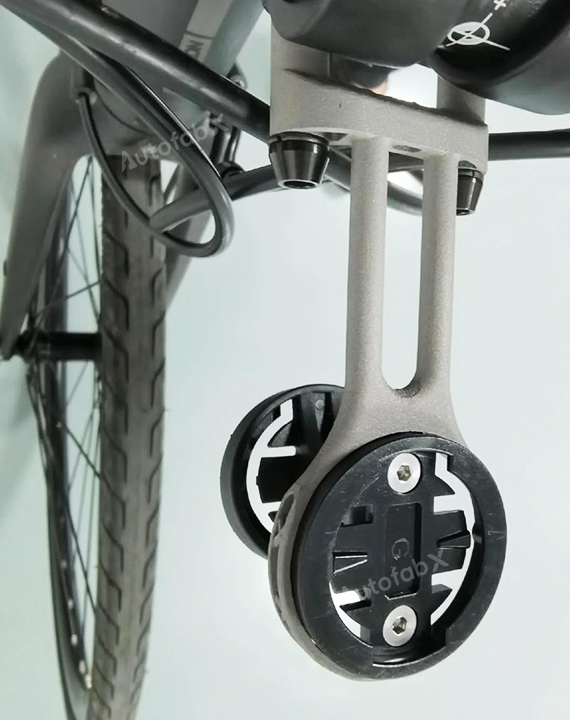
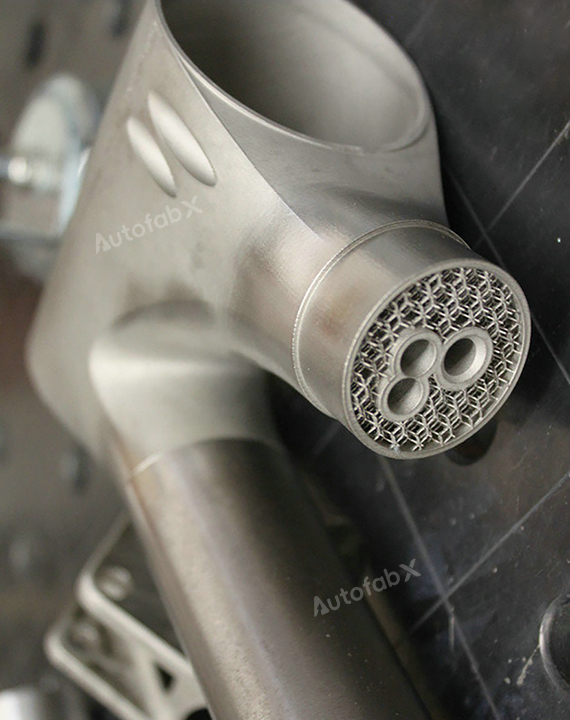
Parts Made by AutofabX