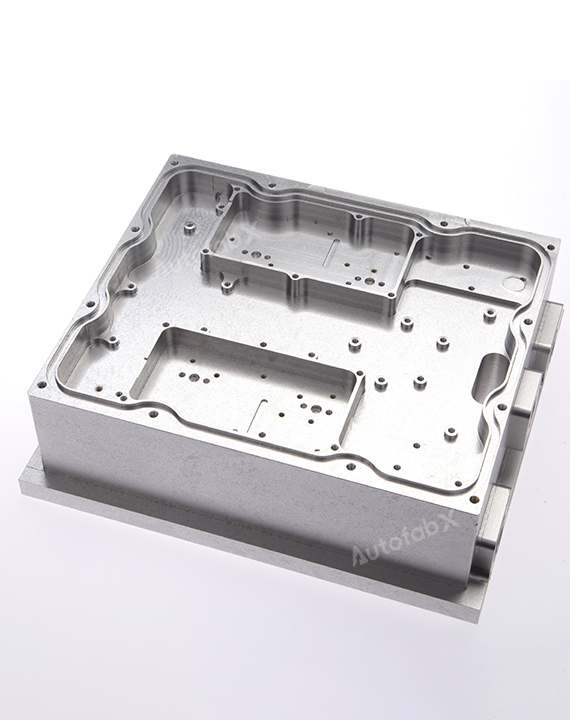
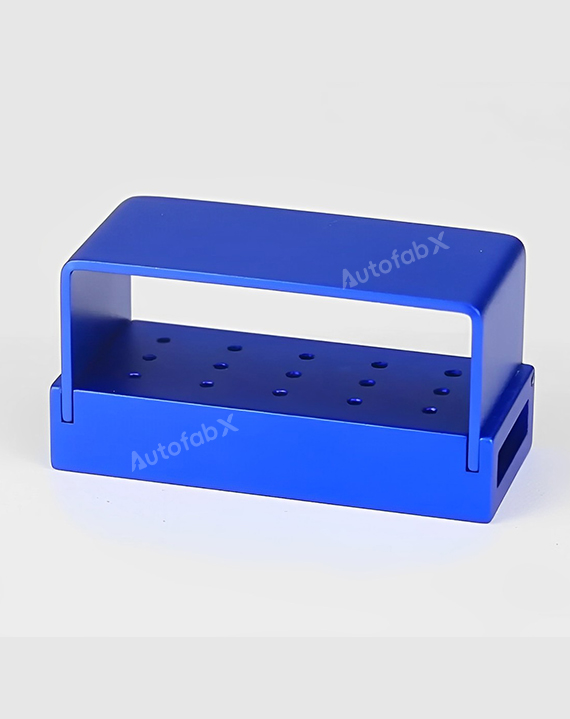
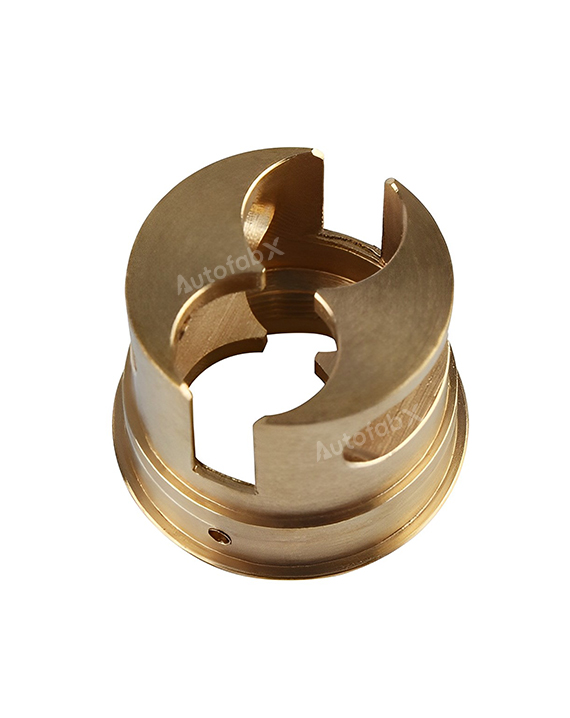
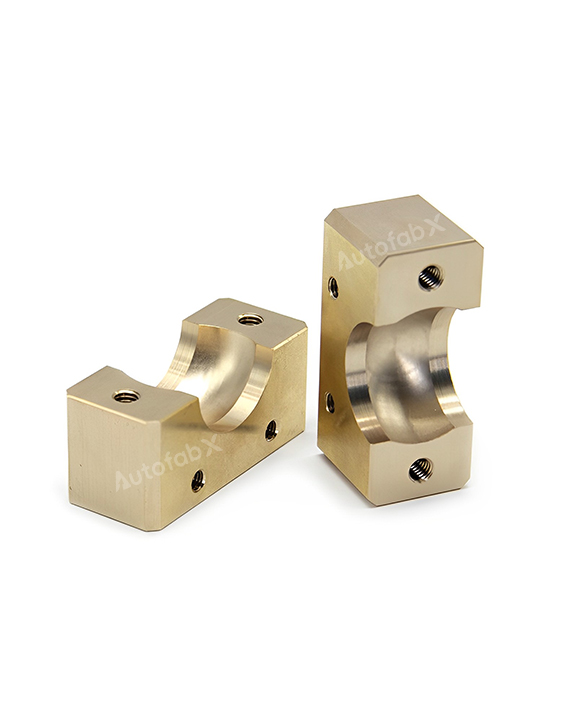
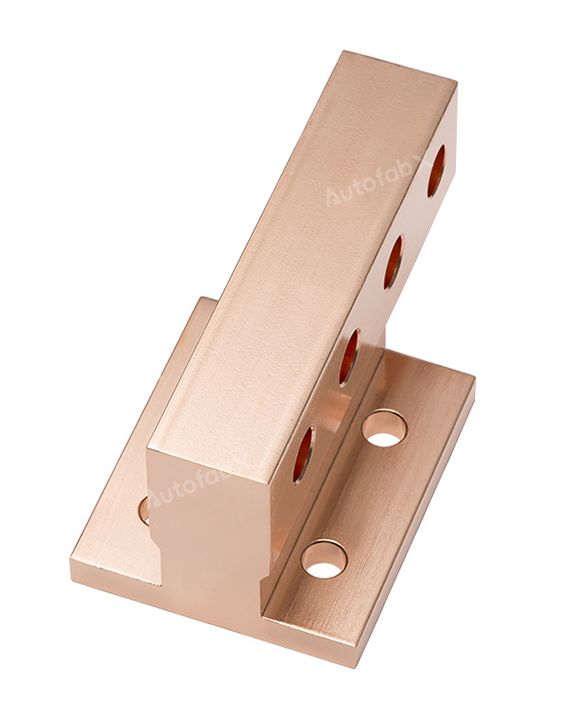
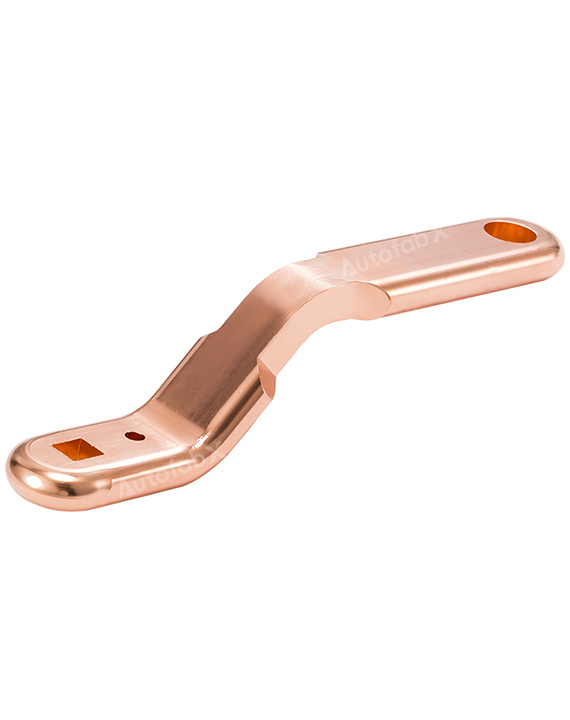
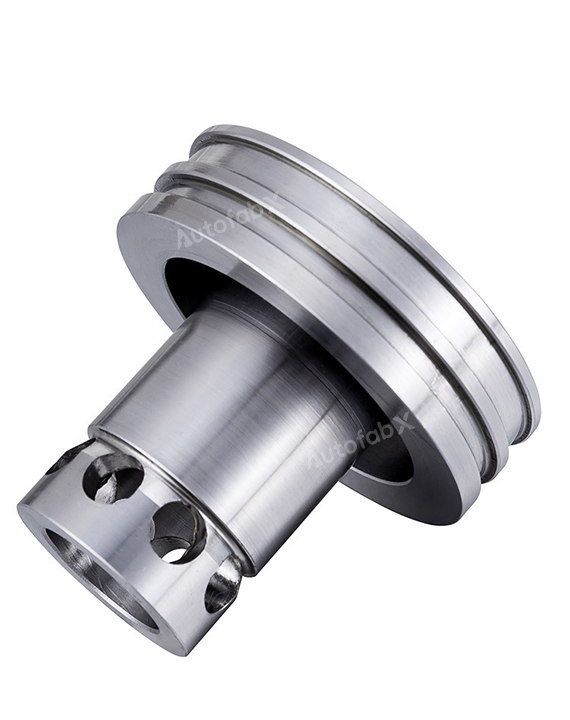
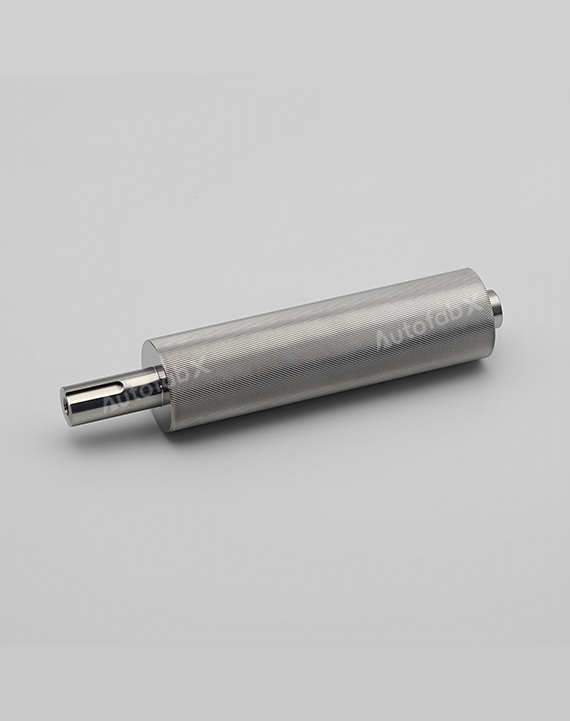
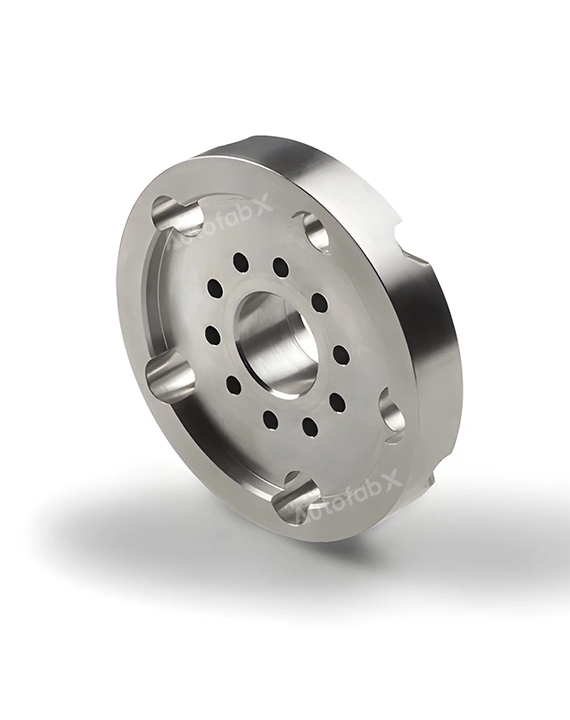
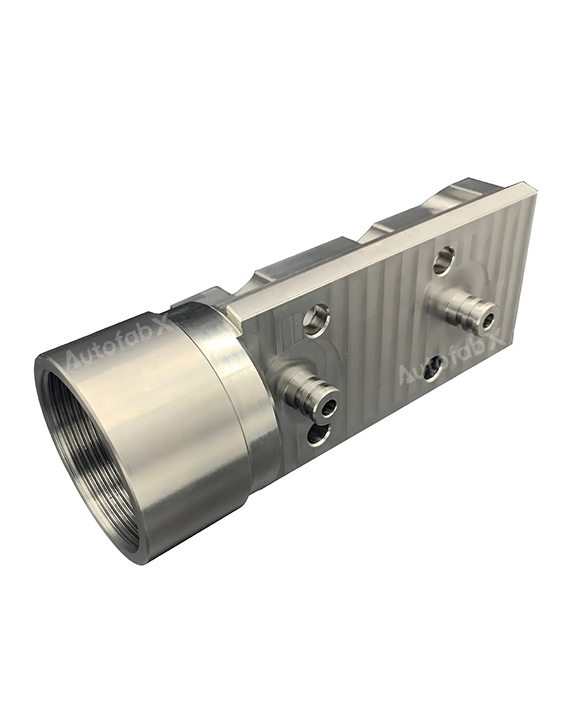
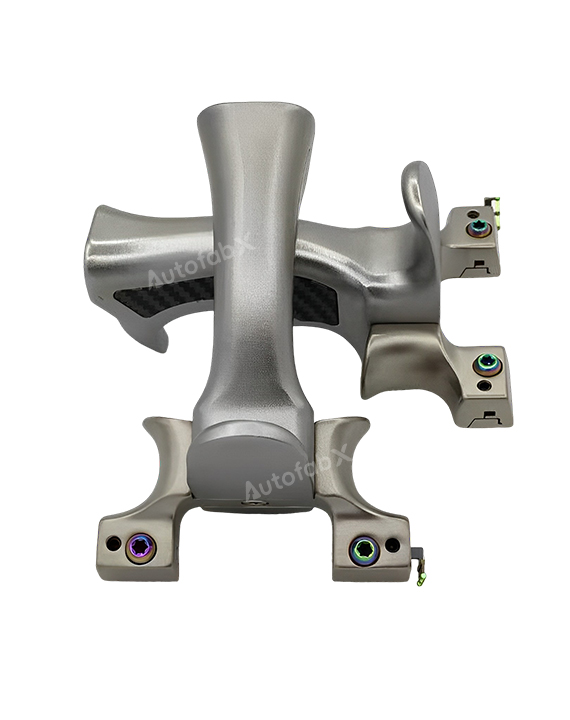
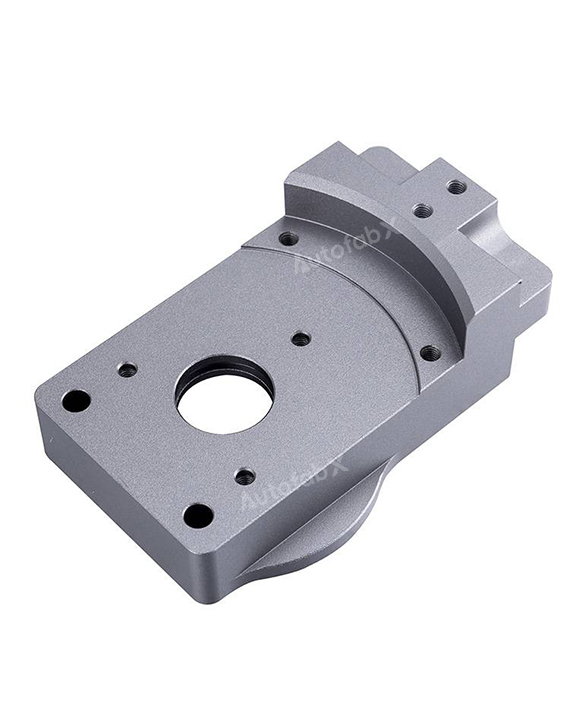
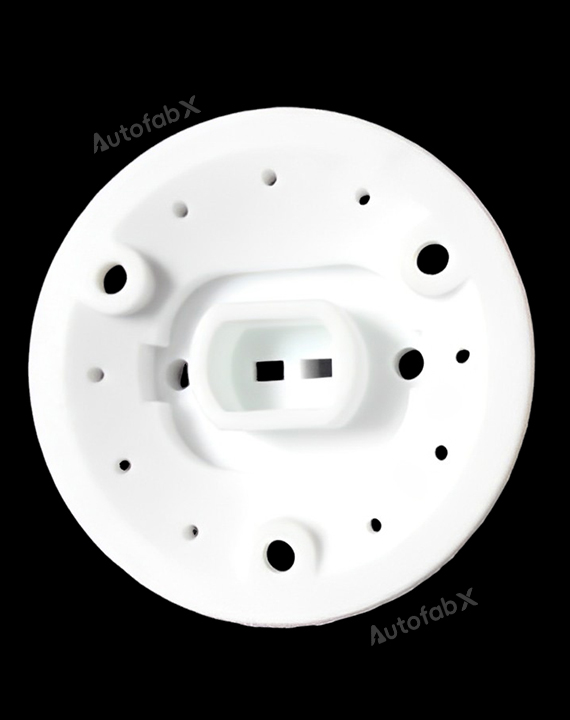
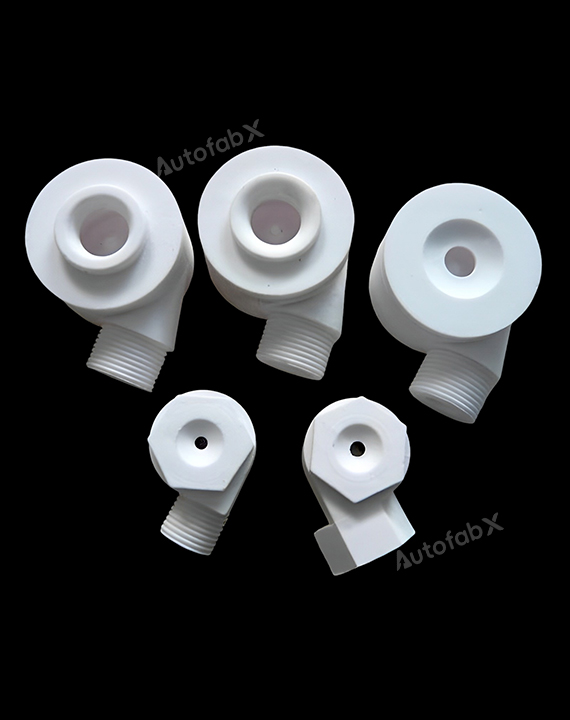
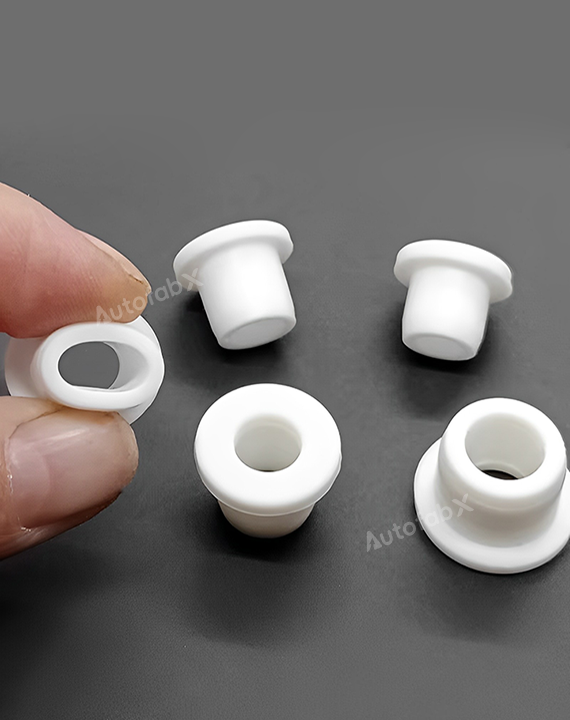
Custom Online CNC Services
Fast turnaround on high-quality CNC parts starts with AutofabX's online service.Get instant quotes in minutes for ISO-certified parts you can trust.
Start A New Quote
STEP | STP | IGS | DWG | DXF | PDF FilesAutofabX CNC Services




CNC Materials
CNC Bronze Alloys
High Wear Resistance, Corrosion Resistance, Excellent Machinability
Finishing:
Passivating, Powder Coating, Electropolishing, Zinc Plating, Silver Plating, Gold Plating, Electroless Nickel Plating, Bead Blasting, Tempering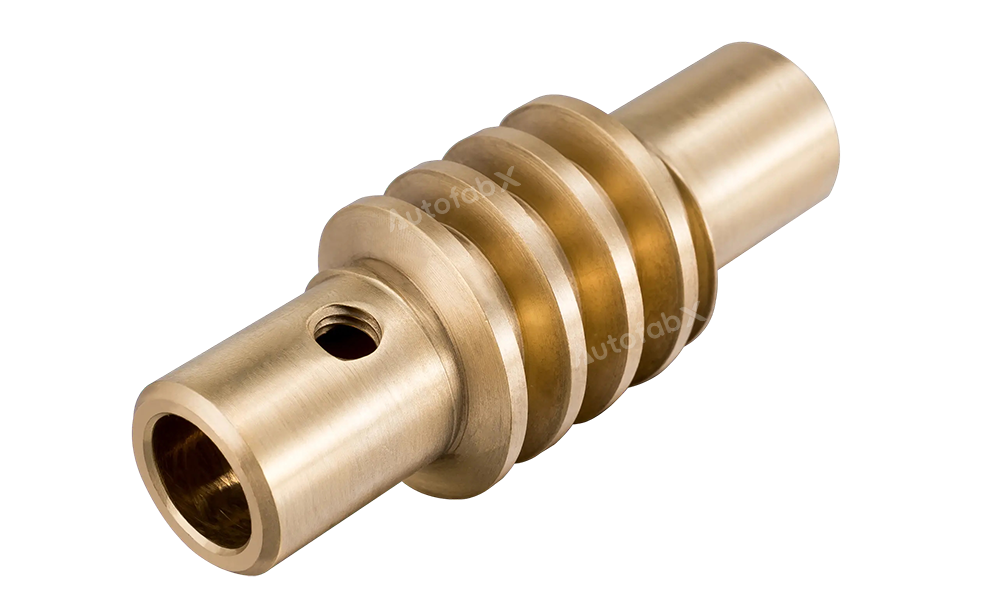
Overview
What is CNC Machining?
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining is a manufacturing process that uses pre-programmed computer software to control the movement of machinery and tools. It is widely used for precision manufacturing, allowing the creation of complex parts with high accuracy. CNC machining can handle a wide range of materials, including metals, plastics, wood, and composites.
Why Choose AutofabX for CNC Services?
AutofabX offers high-quality CNC machining services with a focus on precision, efficiency, and customer satisfaction. Our state-of-the-art facilities and experienced team ensure that parts are manufactured to exact specifications. Key benefits of choosing AutofabX include:
Advanced Equipment: We use the latest CNC machines to achieve high precision and quick turnaround.
Expert Team: Our skilled engineers provide support from design to final production.
Flexible Production: We accommodate both low and high-volume production runs, tailored to customer needs.
Quality Assurance: Rigorous quality checks are in place to ensure parts meet all requirements.
Types of CNC Machining Processes
Milling: Involves rotating cutting tools to remove material from a workpiece. It is ideal for creating complex geometries and fine details.
Turning: Uses a lathe to rotate the workpiece while a cutting tool shapes it, commonly used for cylindrical parts.
Drilling: Creates holes in the workpiece using a rotating drill bit. Drilling is often combined with milling for versatile part creation.
Grinding: Involves abrasive wheels to achieve a smooth finish or precise dimensions.
Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM): Uses electrical sparks to cut intricate shapes in hard materials.
How CNC Machining Works
CNC machining works by converting CAD (Computer-Aided Design) models into CNC programs that control machine operations. These programs dictate the speed, movement, and tooling paths of the machines, ensuring high precision. The basic steps include:
CAD Design: The part is designed in CAD software, creating a 3D model.
CAM Programming: The CAD model is converted to CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing) instructions that generate the toolpaths.
Machine Setup: The material is clamped, and the CNC machine is prepared with the appropriate tooling.
Machining: The CNC machine follows the programmed paths to cut, mill, or drill the material, producing the final part.
Advantages and Limitations of CNC Machining
Advantages:
Precision and Accuracy: CNC machines can achieve extremely tight tolerances, making them ideal for high-precision applications.
Repeatability: CNC machining allows for consistent production of identical parts, ensuring uniformity.
Versatility: Capable of machining a wide range of materials and producing complex geometries.
Automation: Reduces the need for manual intervention, increasing efficiency and reducing errors.
Scalability: Suitable for both prototyping and large-scale production.
Limitations:
Cost: Initial setup and programming can be costly, making CNC machining less economical for very low-volume production.
Material Waste: Subtractive nature leads to material wastage compared to additive manufacturing.
Complexity Limits: Some complex internal geometries may be challenging or impossible to achieve with CNC alone.
CNC Machining Design Guidance Table
| Design Aspect | Recommendation |
| Minimum Wall Thickness | 1.0 mm |
| Minimum Drill Hole Size | 0.8 mm |
| Maximum Part Size | 1000 mm x 500 mm x 500 mm |
| Tolerances | ±0.05 mm |
| Corner Radii | Minimum 0.5 mm radius |
| Thread Depth | Max depth of 3x the diameter |
| Surface Finish | Specify requirements based on application |
CNC Machining Precision Table
| Machining Operation | Typical Tolerance |
| Milling | ±0.05 mm |
| Turning | ±0.02 mm |
| Drilling | ±0.08 mm |
| Grinding | ±0.01 mm |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about CNC Machining
What materials can be machined using CNC?
CNC machining can work with a variety of materials, including metals (aluminum, steel, titanium), plastics (ABS, nylon, polycarbonate), and composites.
What are the typical lead times for CNC machining?
Lead times vary depending on the complexity of the part and the volume, but typically range from 3 to 10 days.
What is the maximum part size for CNC machining?
The maximum part size depends on the machine capabilities. At AutofabX, we can handle parts up to 1000 mm x 500 mm x 500 mm.
How accurate is CNC machining?
CNC machining can achieve very high precision, with tolerances as tight as ±0.01 mm depending on the operation.
Is CNC machining suitable for prototyping?
Yes, CNC machining is ideal for prototyping, especially when high precision and a good surface finish are required.
What industries commonly use CNC machining?
CNC machining is used in industries such as aerospace, automotive, medical, electronics, and consumer products.
How do I ensure my design is suitable for CNC machining?
Ensure your design follows best practices such as maintaining uniform wall thickness, avoiding sharp internal corners, and specifying appropriate tolerances.
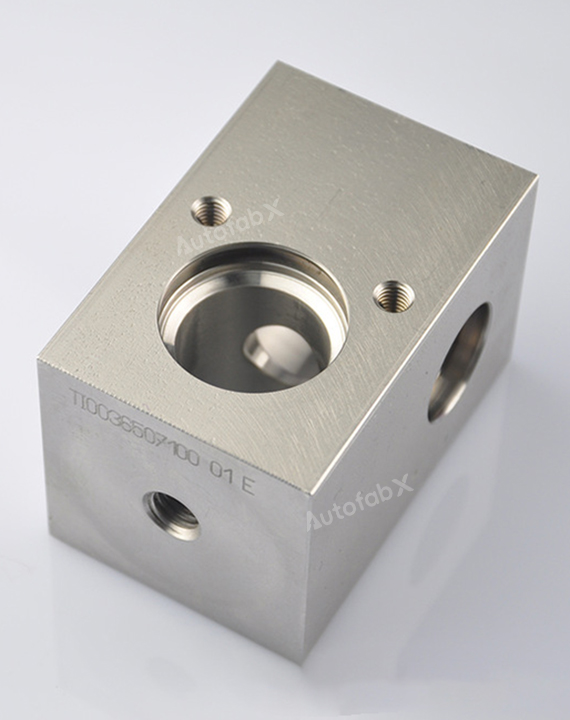
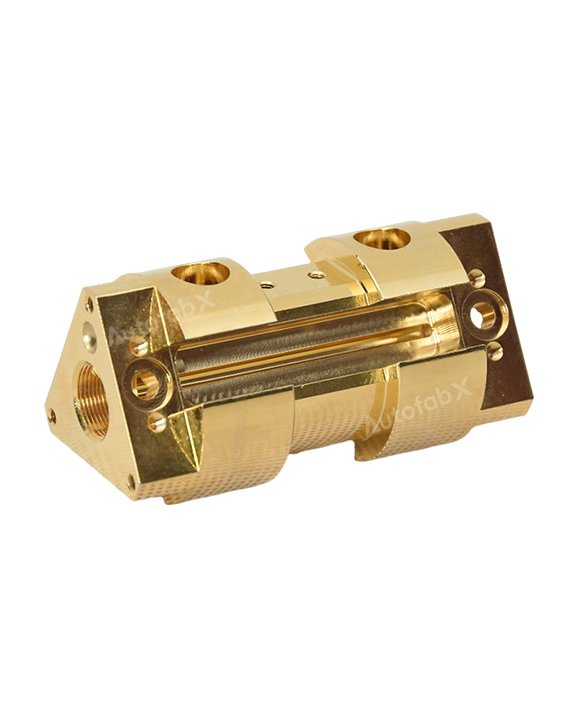
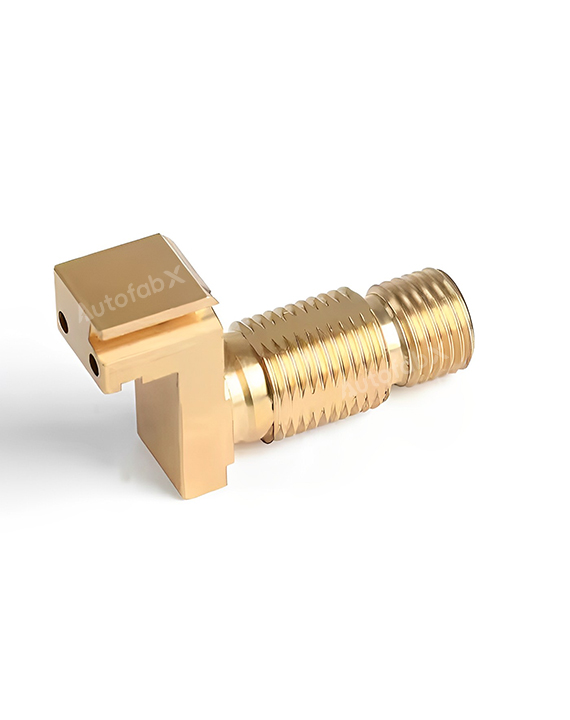
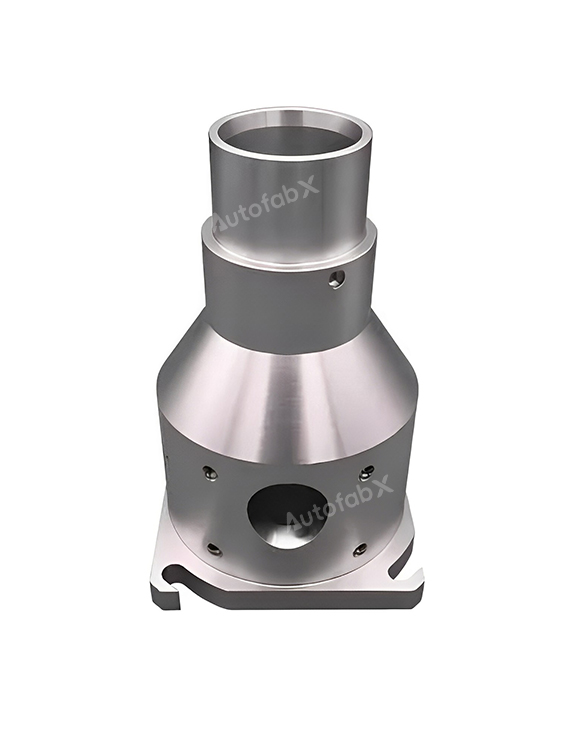
Parts Made by AutofabX