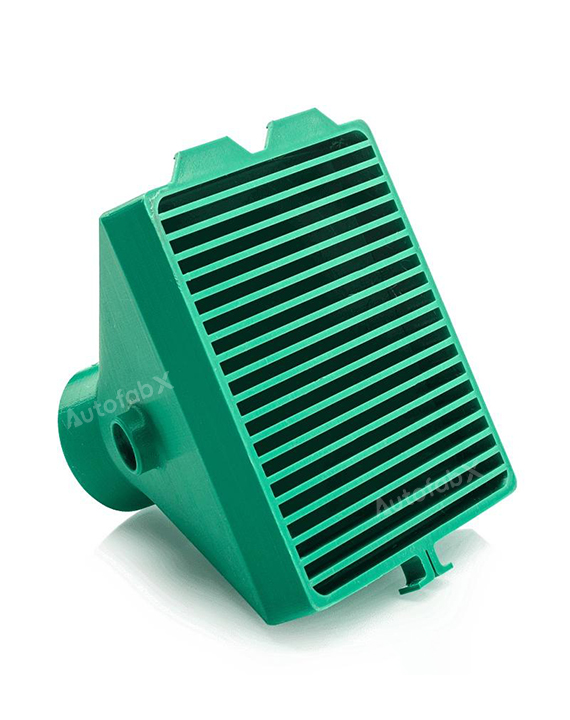
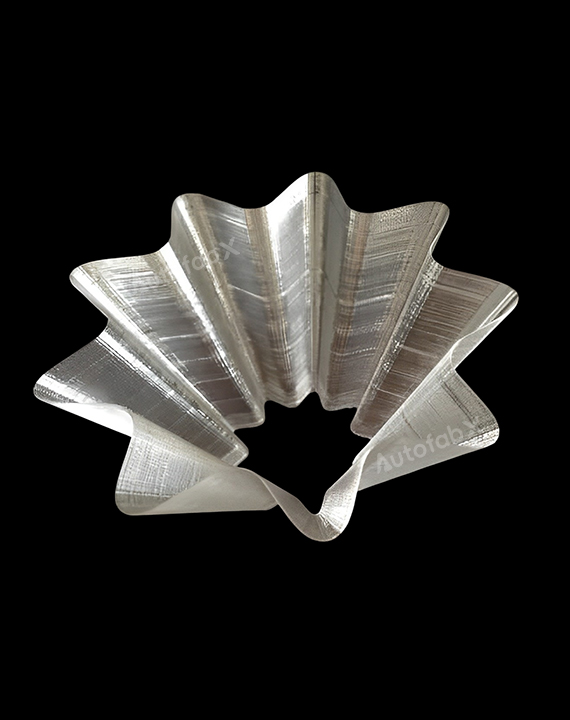
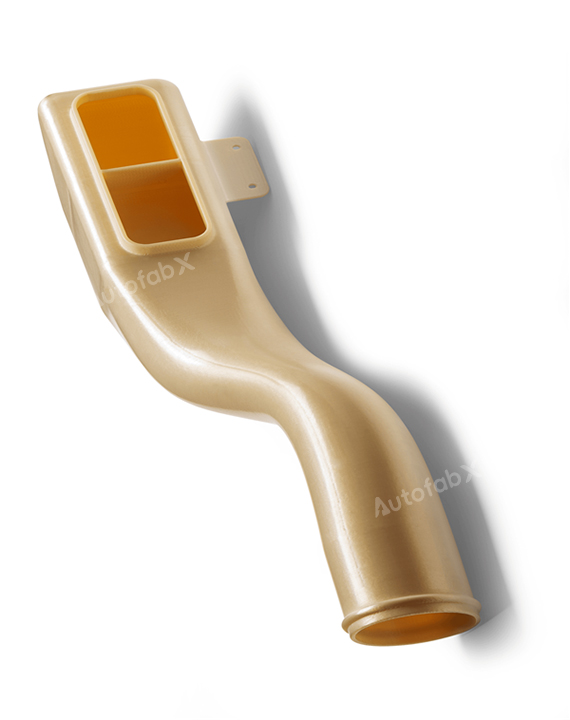
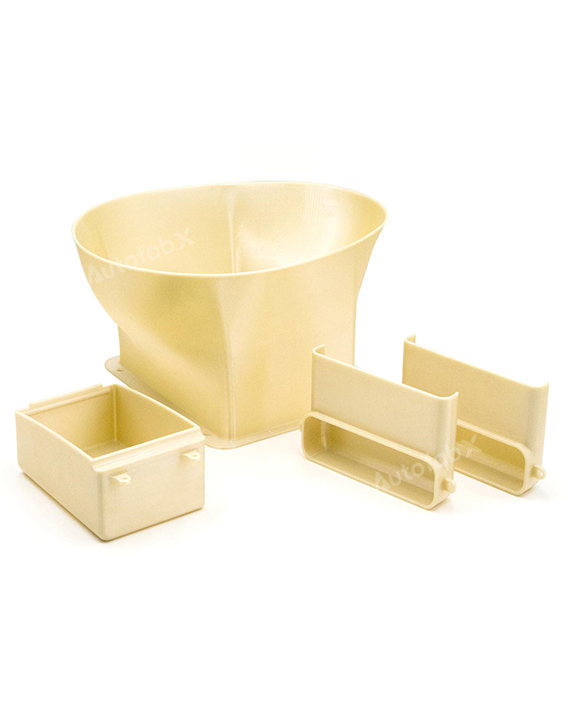
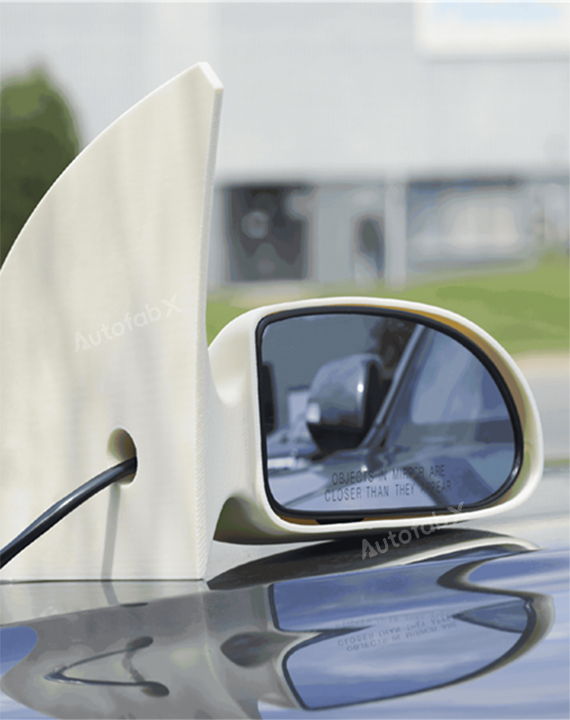
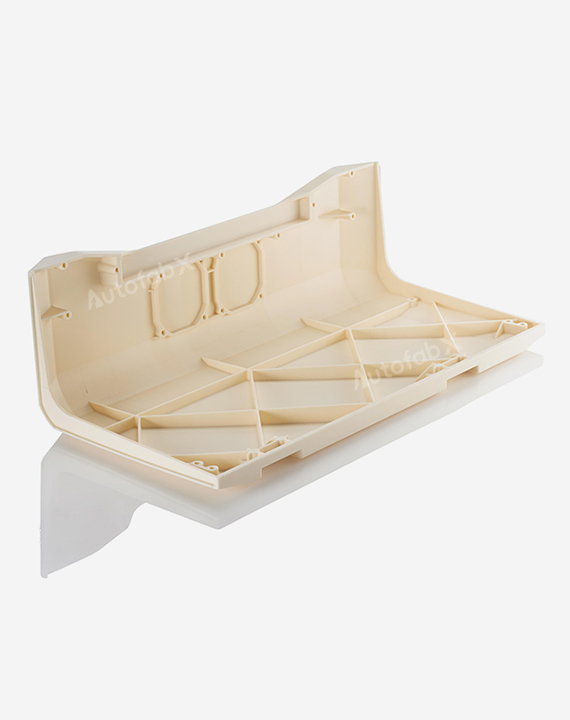
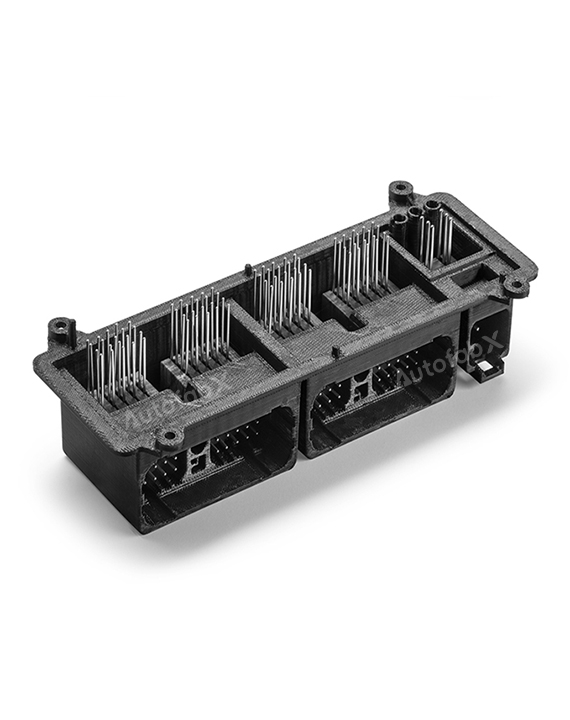
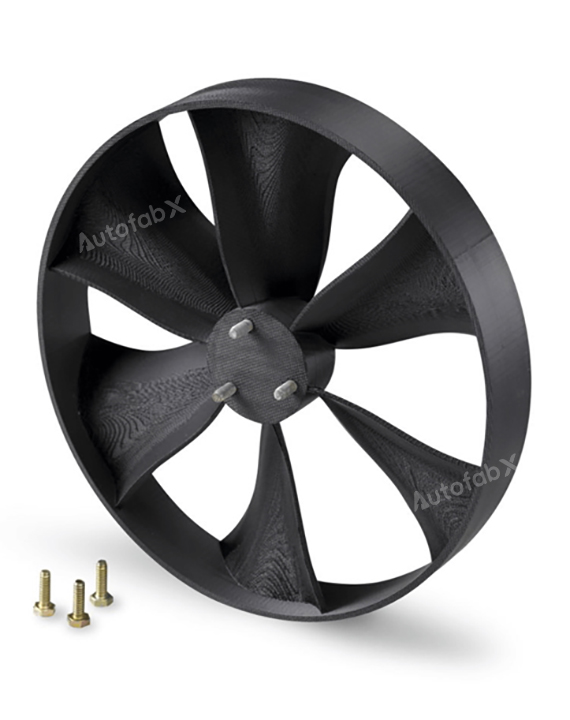
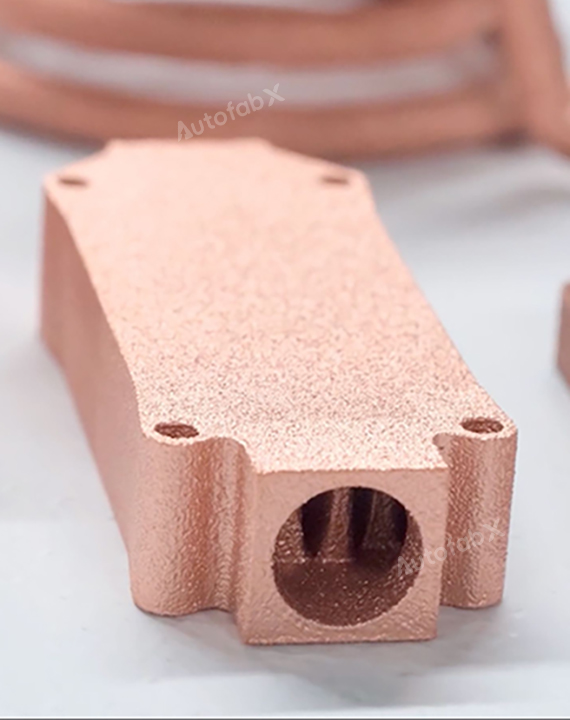
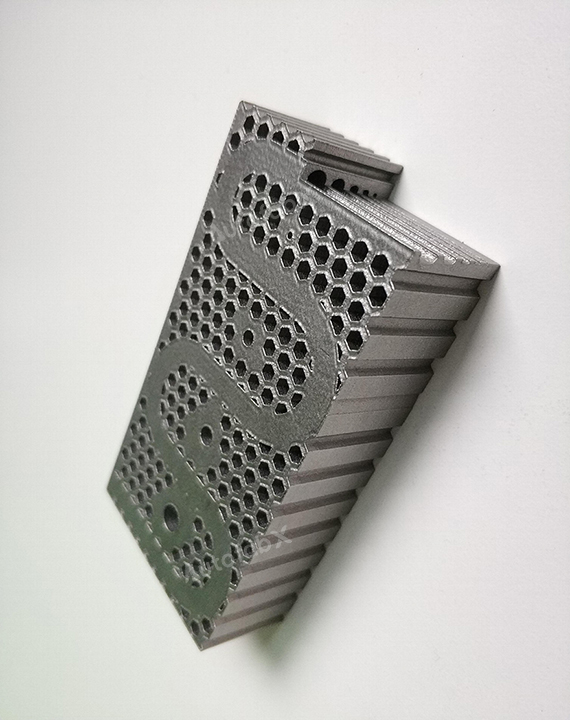
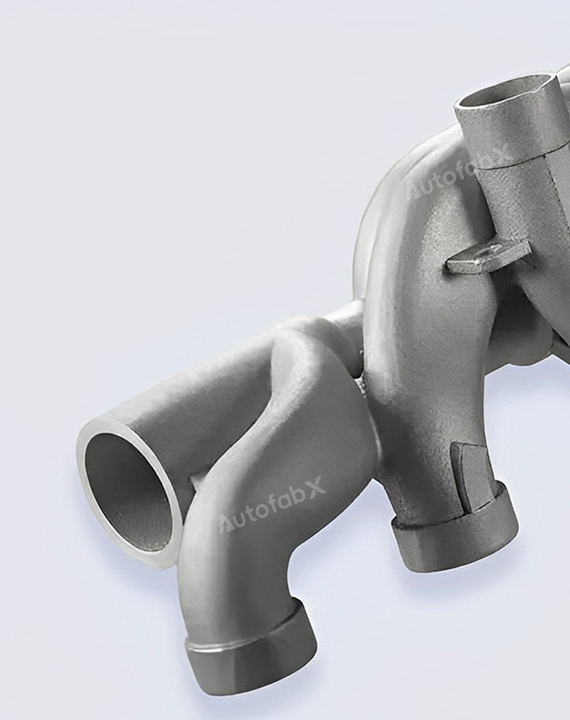
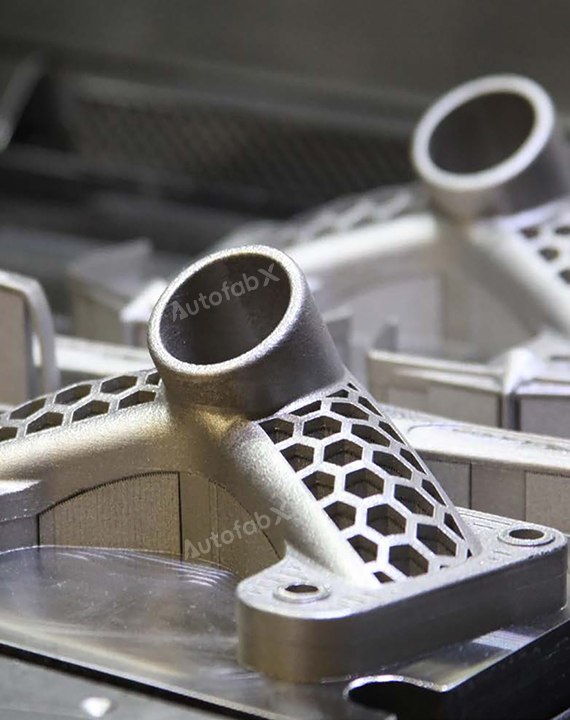
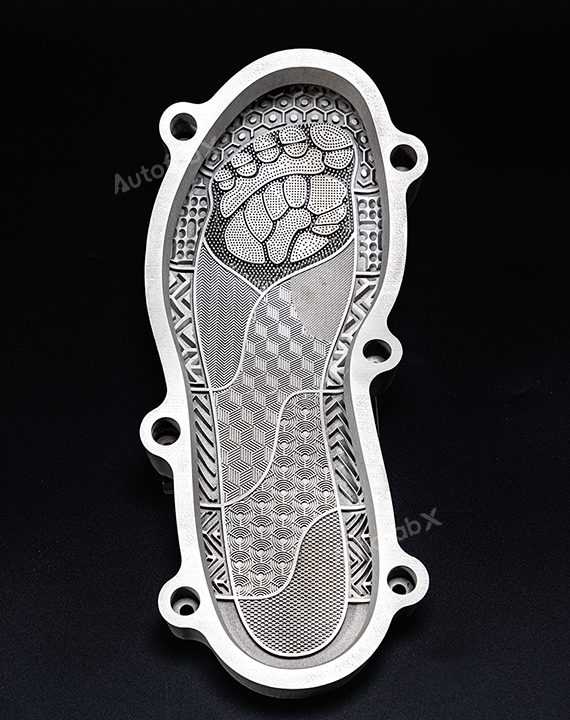
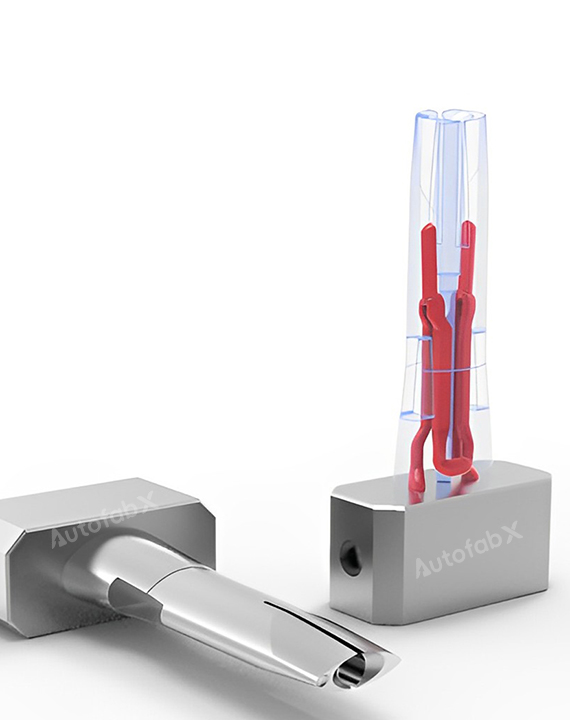
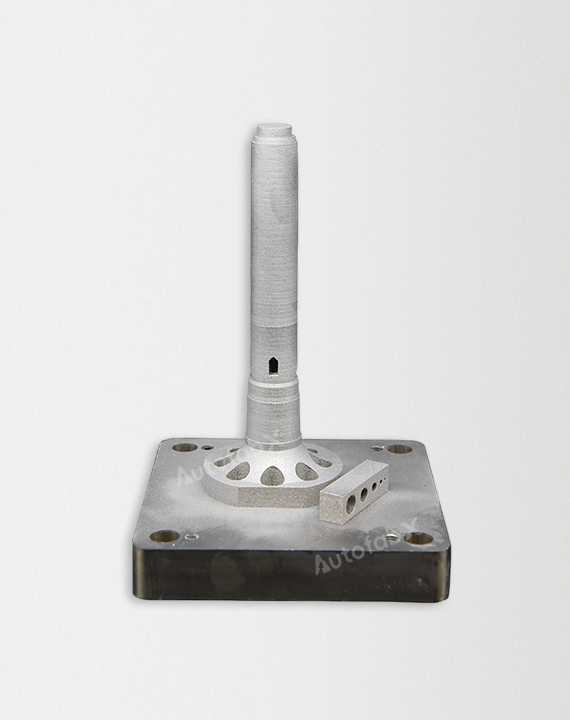
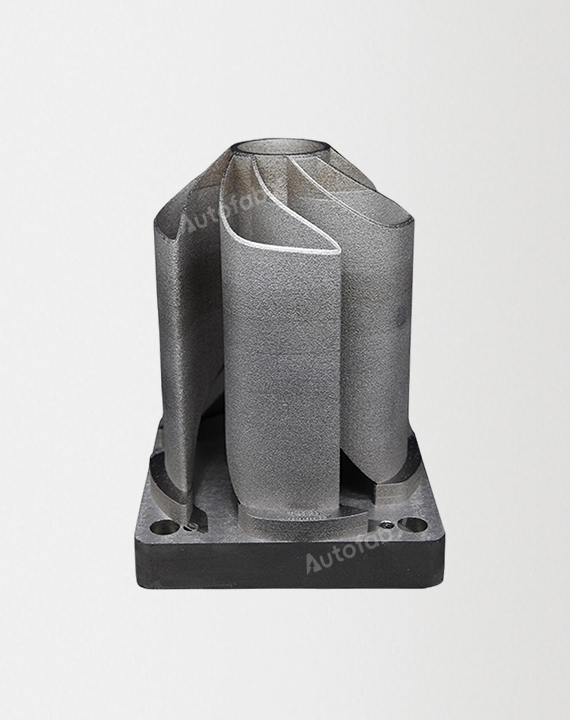
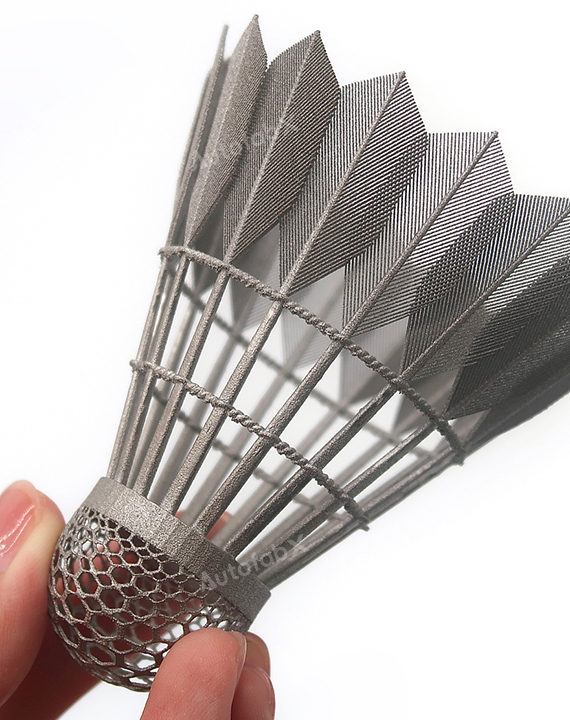
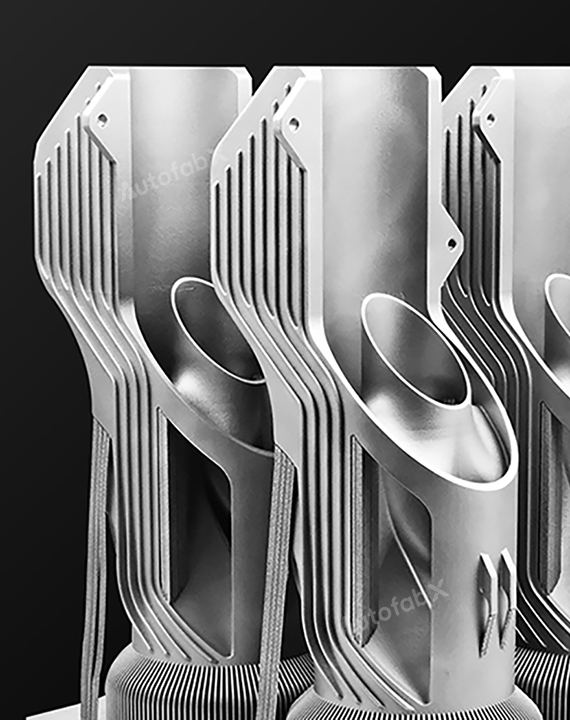
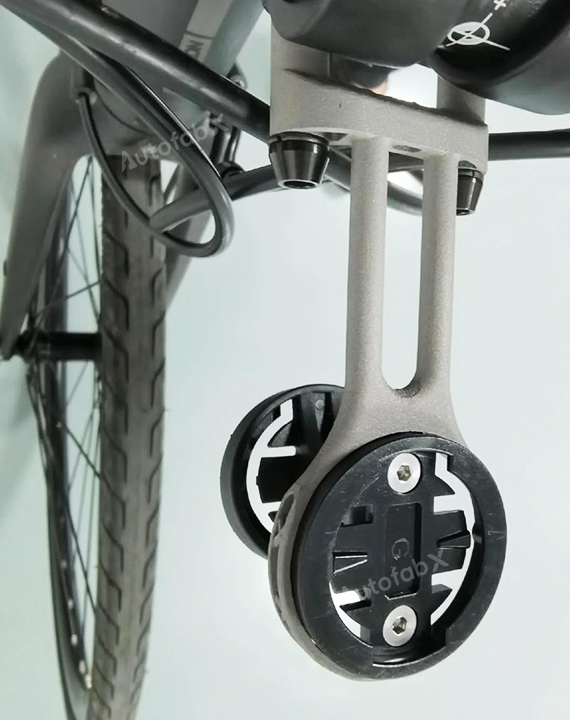
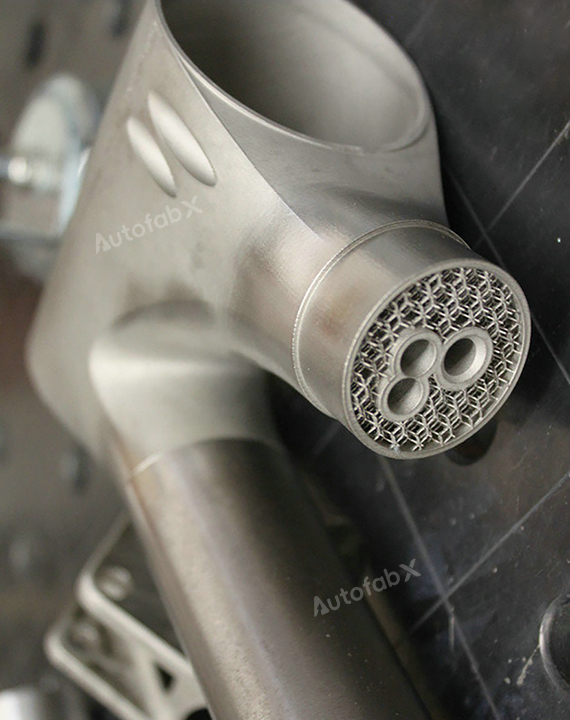
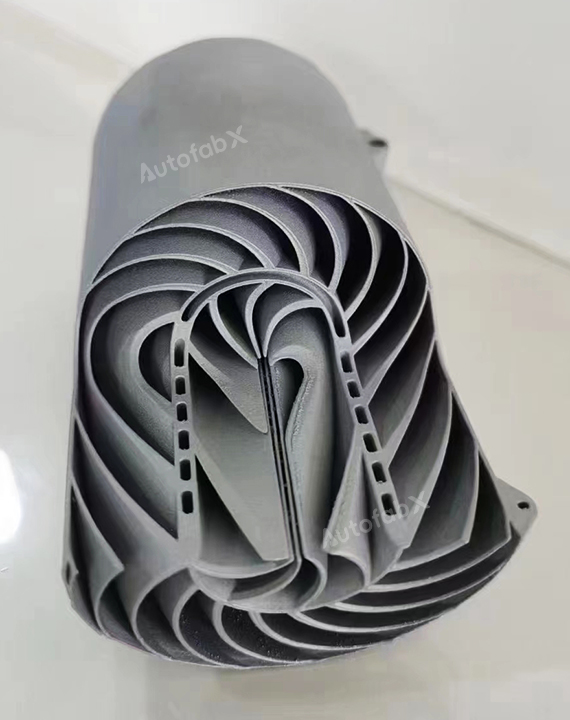
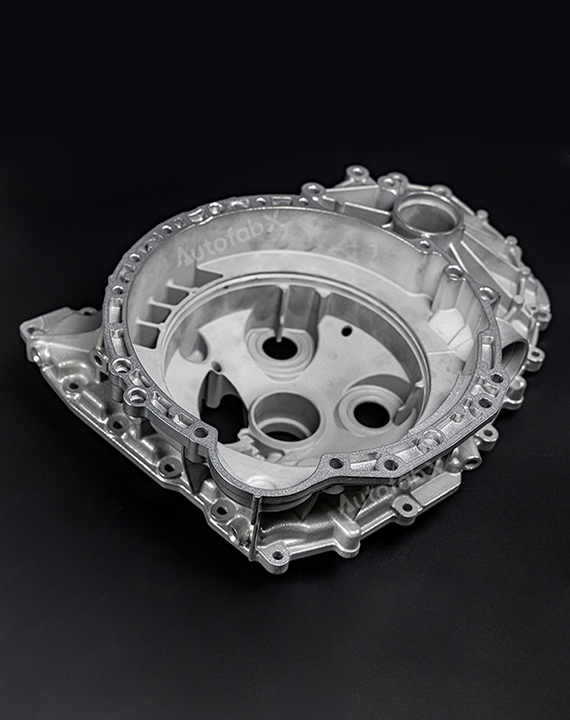
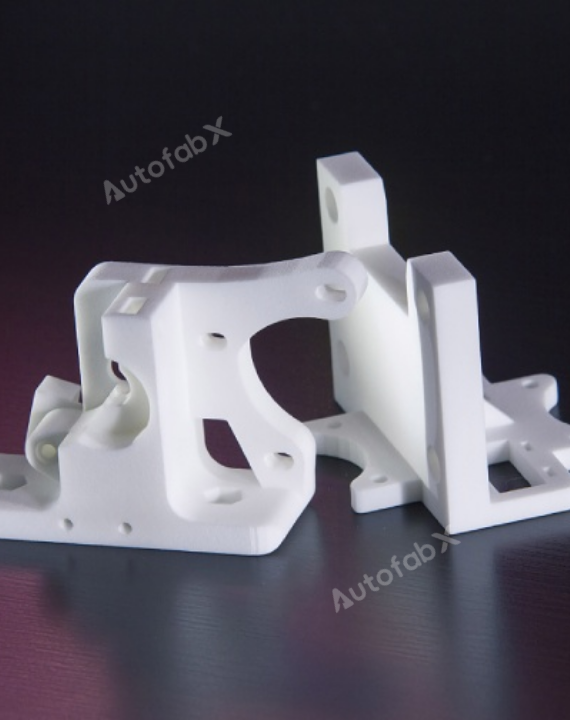
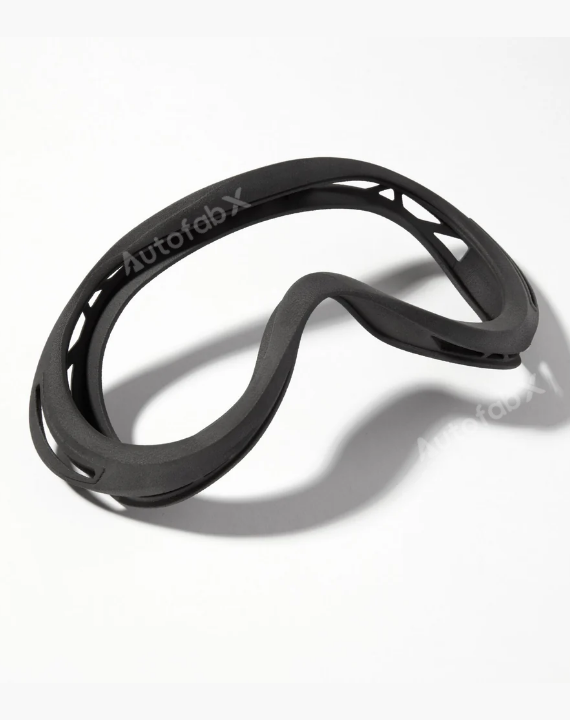
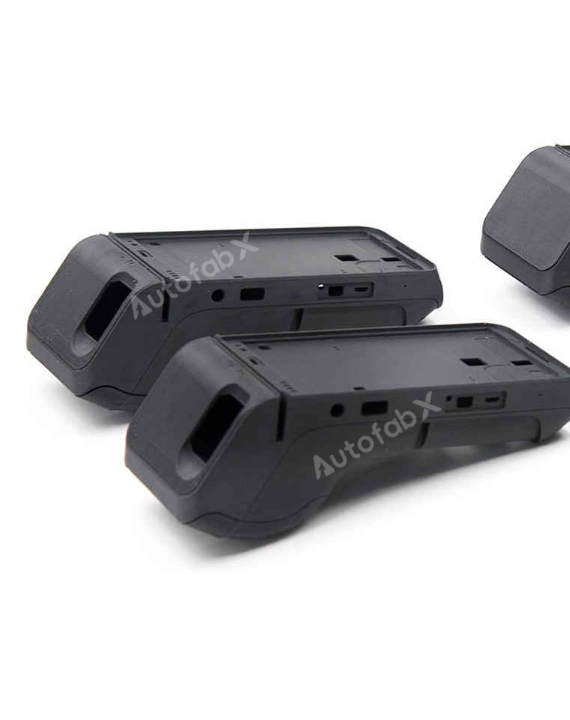
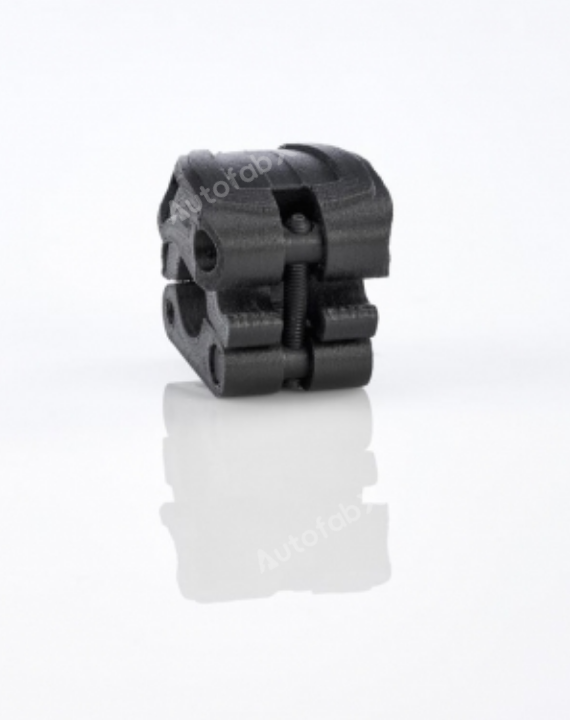
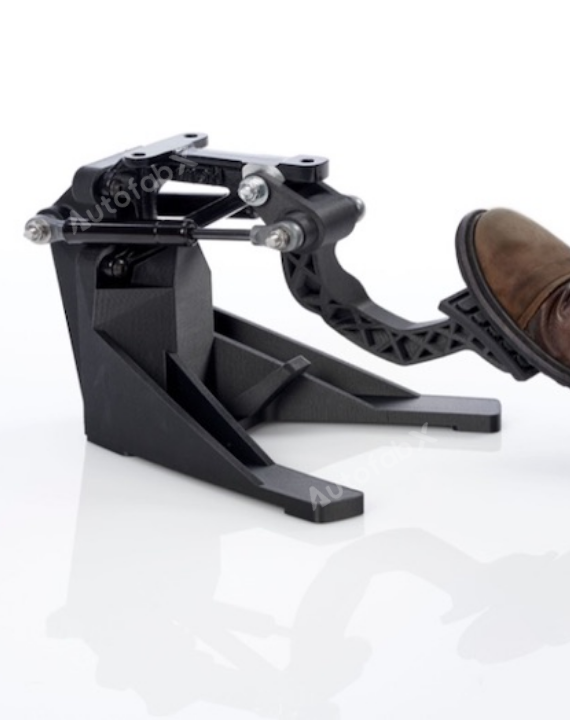
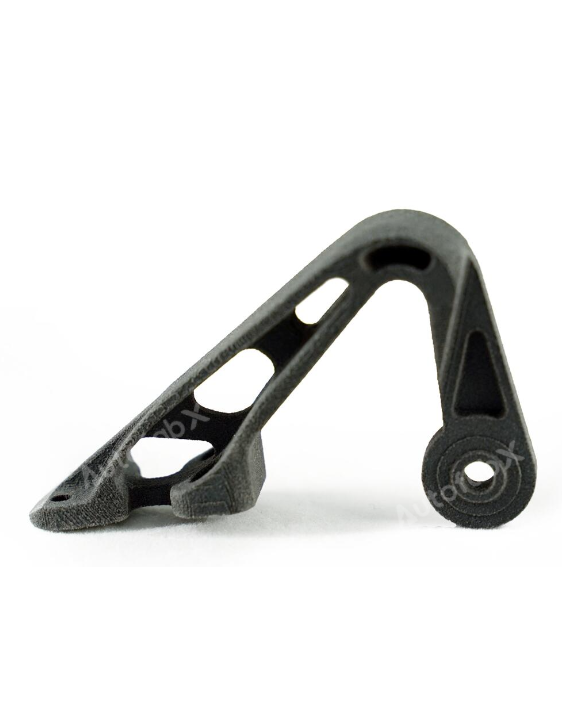
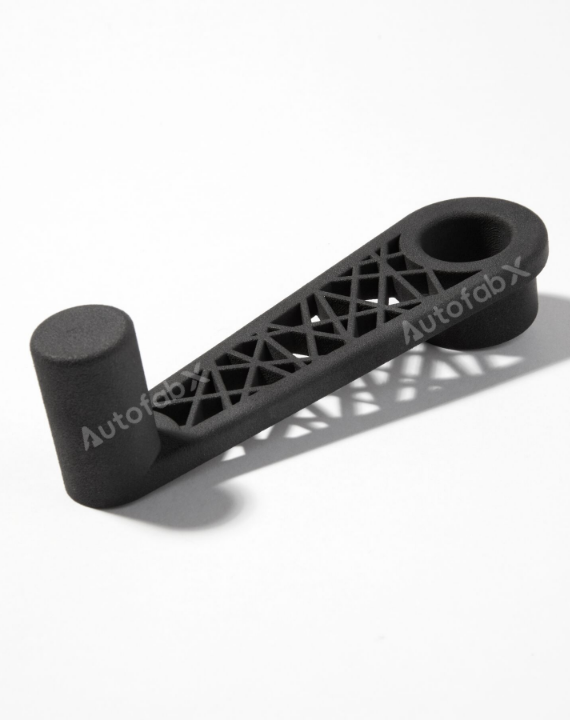
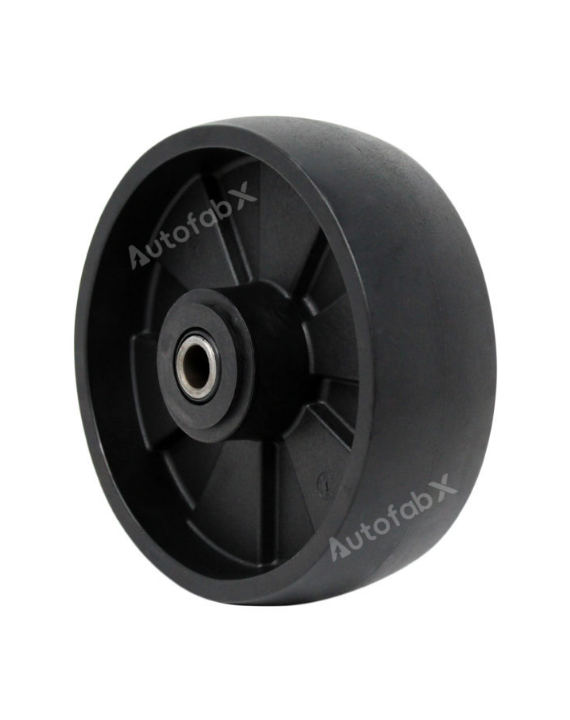
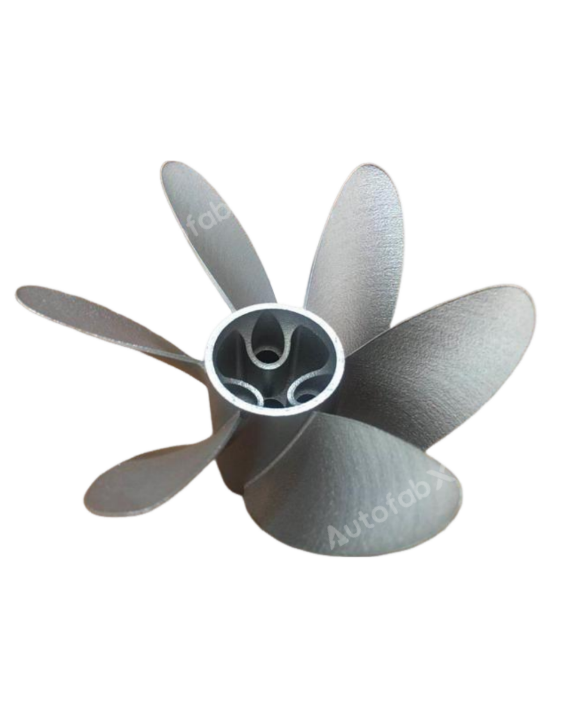
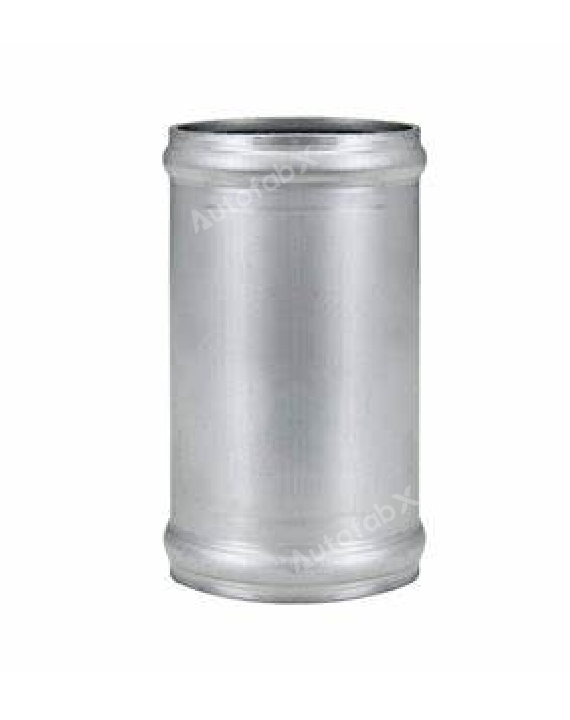
Custom Online 3D Printing Services
Wide Range of Materials, Advanced Technology, Expert Guidance
Start A New Quote
STEP | STP | IGS | DWG | DXF | PDF FilesAutofabX 3D Printing Services














3D Printing Materials
BJ Stainless Steel 17-4PH
High Strength and Corrosion Resistance, Cost-Effective Metal Printing, Complex Geometries
Finishing:
Laser Engraving, Sand Blasting, Shot Peening , Heat Treatment, Polishing, Anodizing
Overview
What is 3D Printing?
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is a process of creating three-dimensional objects from a digital file by laying down successive layers of material. It enables the production of complex geometries that would be difficult or impossible to achieve using traditional manufacturing methods.
Why Choose AutofabX for 3D Printing Services?
AutofabX provides high-quality 3D printing services with a focus on precision, efficiency, and customization. Reasons to choose AutofabX include:
Wide Range of Materials: We offer a variety of materials, including plastics, metals, and composites, to suit different application needs.
Advanced Technology: Our state-of-the-art 3D printers ensure high precision and quality, producing parts with excellent accuracy and surface finish.
Expert Guidance: Our team of engineers assists clients in optimizing their designs for additive manufacturing, ensuring the best possible results.
Fast Turnaround: We provide quick production times, allowing clients to get their parts faster and accelerate their projects.
Types of 3D Printing Processes
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM): This process uses a continuous filament of thermoplastic material, which is heated and extruded layer by layer to create the part.
Stereolithography (SLA): SLA uses a laser to cure liquid resin into solid plastic, producing high-resolution parts with smooth surfaces.
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS): SLS uses a laser to fuse powdered materials, such as nylon, into solid structures, suitable for functional prototypes and complex geometries.
Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS): DMLS is used for metal 3D printing, where a laser fuses metal powder to create fully dense, functional metal parts.
PolyJet: This process uses inkjet technology to spray liquid photopolymer layer by layer, offering high detail and a variety of material properties.
How 3D Printing Works
Design: The process begins with creating a 3D model using CAD software.
Slicing: The 3D model is sliced into thin layers, and the slicing software generates instructions for the printer.
Printing: The printer follows the instructions to build the object layer by layer, using the selected material.
Post-Processing: After printing, the part may require post-processing, such as cleaning, curing, or surface finishing, depending on the material and printing process.
Advantages and Limitations of 3D Printing
Advantages:
Design Flexibility: 3D printing allows the creation of complex geometries and customized designs that are difficult to achieve with traditional manufacturing.
Rapid Prototyping: Fast production times make 3D printing ideal for prototyping, enabling designers to iterate quickly.
Reduced Waste: Additive manufacturing only uses the material needed to create the part, resulting in minimal waste.
Cost-Effective for Small Batches: 3D printing can be more cost-effective for low-volume production compared to traditional manufacturing.
Limitations:
Material Limitations: Not all materials are suitable for 3D printing, and the selection can be limited compared to traditional manufacturing.
Surface Finish: Depending on the printing process, parts may have visible layer lines and may require additional finishing.
Strength and Durability: 3D-printed parts may not have the same strength or durability as those made with traditional methods, depending on the material and process used.
3D Printing Design Guidance Table
| Design Aspect | Recommendation |
| Minimum Wall Thickness | 1.0 mm |
| Minimum Feature Size | 0.8 mm |
| Overhangs | Use support for angles > 45° |
| Tolerance | ±0.2 mm |
| Layer Height | 0.1-0.3 mm |
3D Printing Precision Table
| Printing Process | Typical Tolerance |
| FDM | ±0.5 mm |
| SLA | ±0.1 mm |
| SLS | ±0.3 mm |
| DMLS | ±0.1 mm |
| PolyJet | ±0.05 mm |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about 3D Printing
What materials can be used in 3D printing?
3D printing can use a variety of materials, including plastics, metals, ceramics, and composites, depending on the printing process.
Is 3D printing suitable for large-scale production?
3D printing is generally more suitable for prototyping and low-volume production. For large-scale production, traditional manufacturing methods may be more cost-effective.
How strong are 3D-printed parts?
The strength of 3D-printed parts depends on the material and printing process used. While some parts can be strong, they may not match the strength of traditionally manufactured parts.
What industries benefit from 3D printing?
Industries such as aerospace, automotive, healthcare, and consumer goods benefit from the design flexibility, rapid prototyping, and customization offered by 3D printing.
What post-processing is required for 3D-printed parts?
Post-processing can include cleaning, curing, sanding, or painting, depending on the material and desired finish of the part.
How accurate is 3D printing?
Accuracy depends on the 3D printing process. SLA and DMLS generally provide the highest accuracy, while FDM may have lower precision.
Can 3D printing be used for functional parts?
Yes, 3D printing can be used to produce functional parts, especially with processes like SLS and DMLS, which offer good mechanical properties.
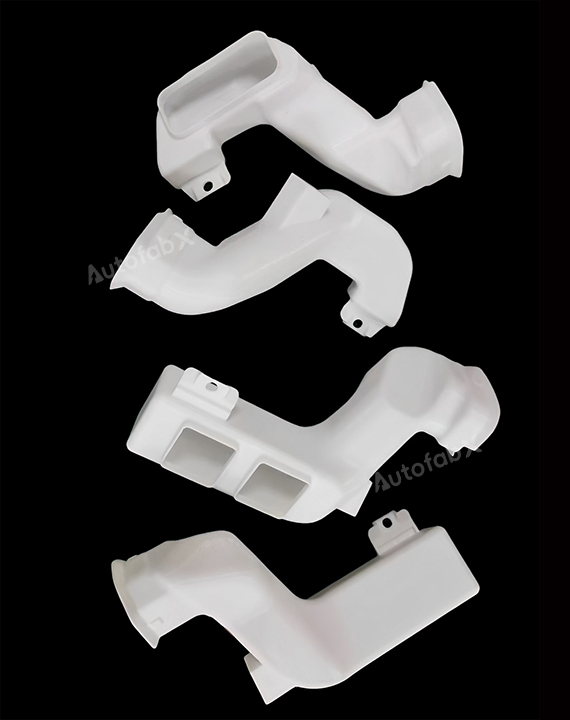
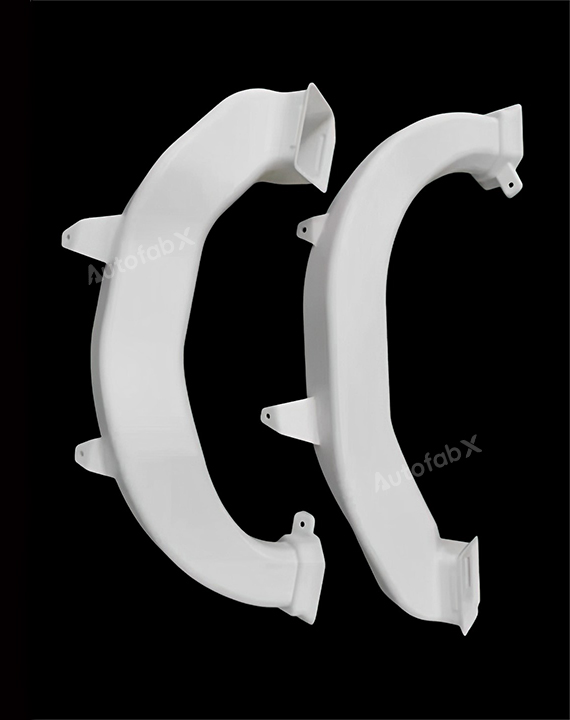
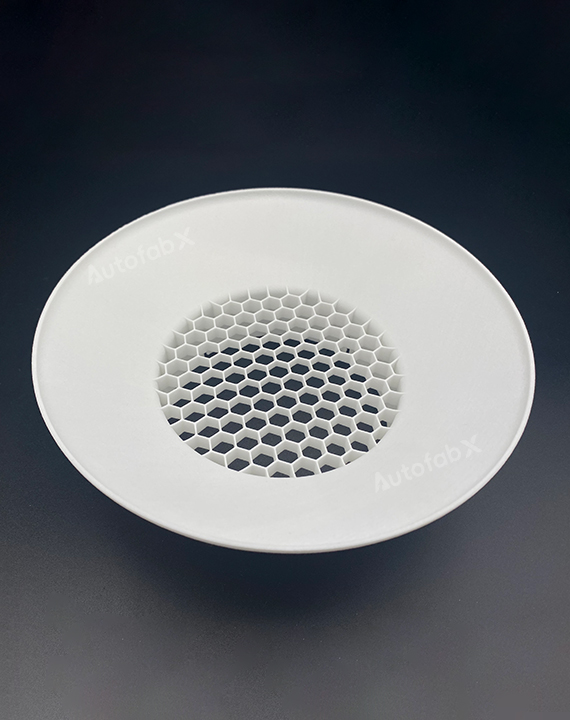
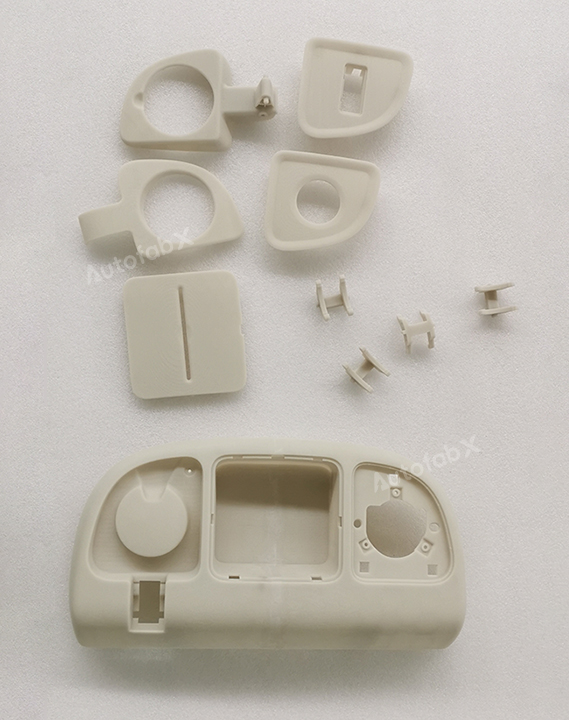
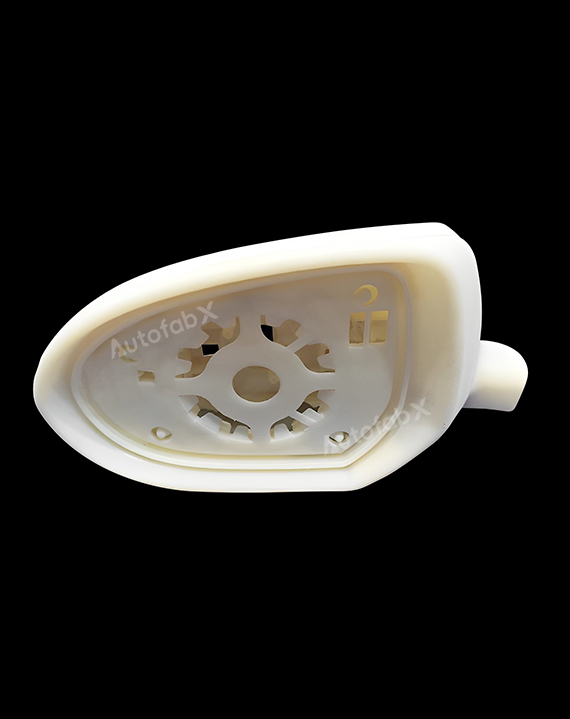
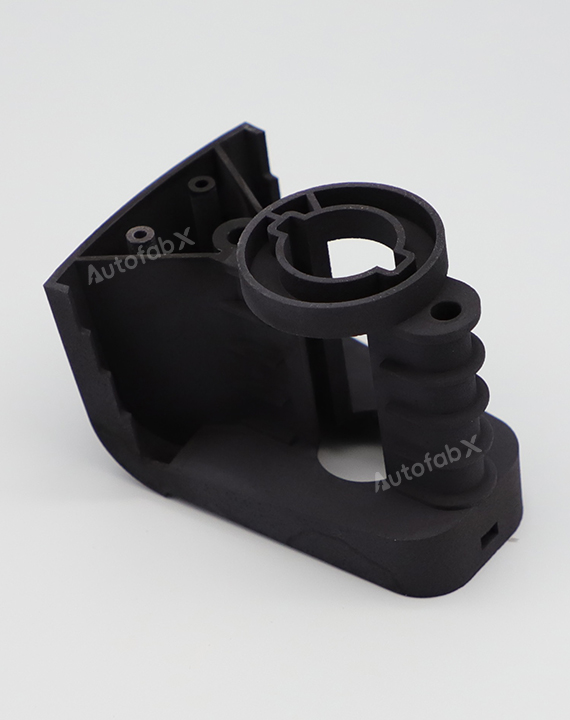
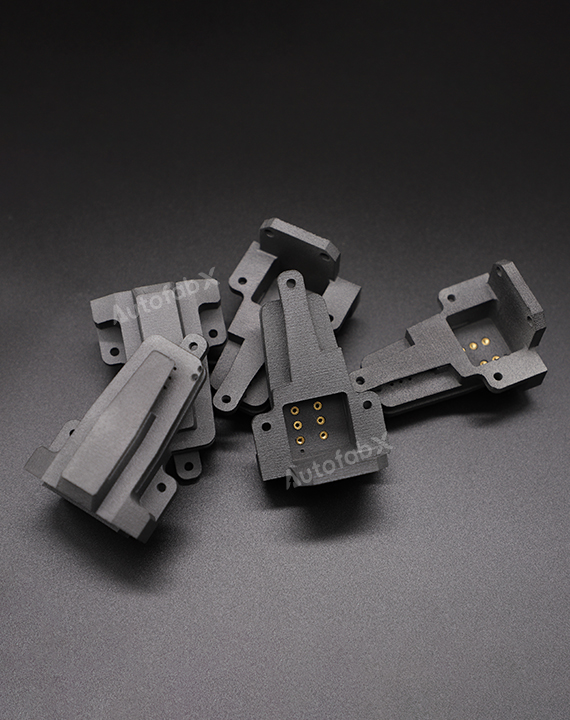
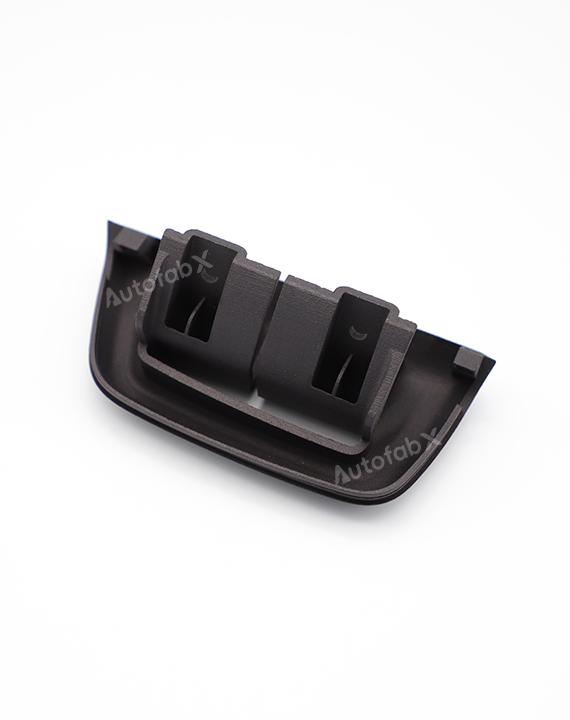
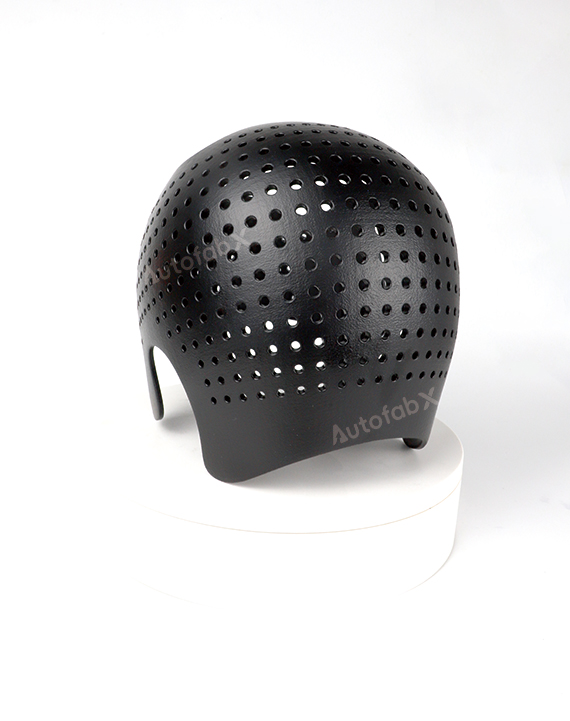
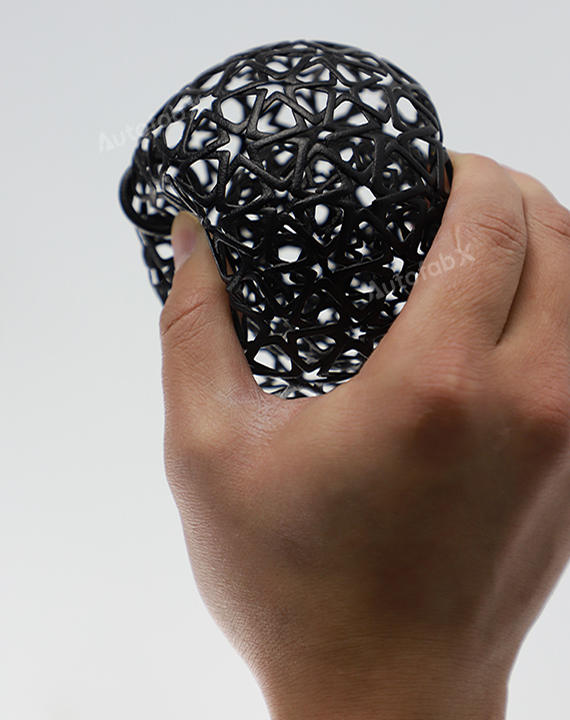
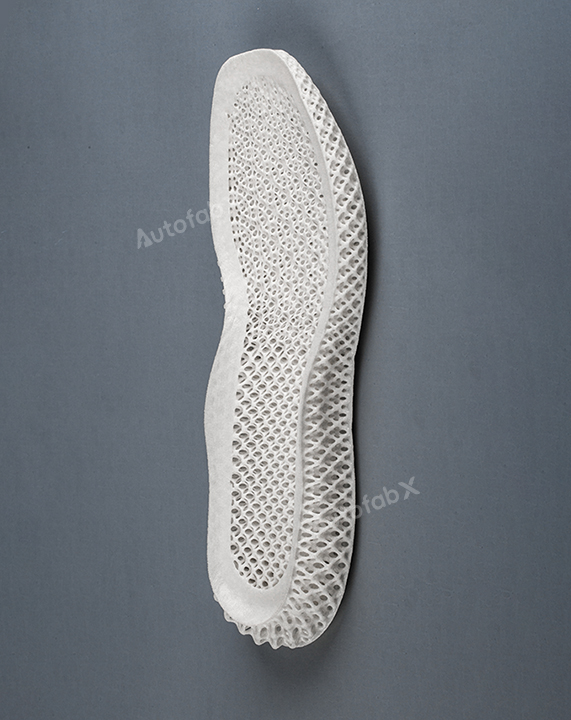
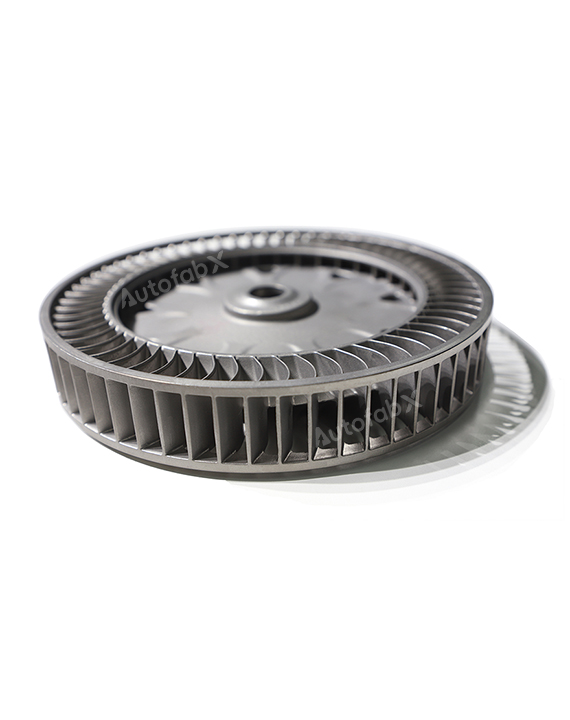
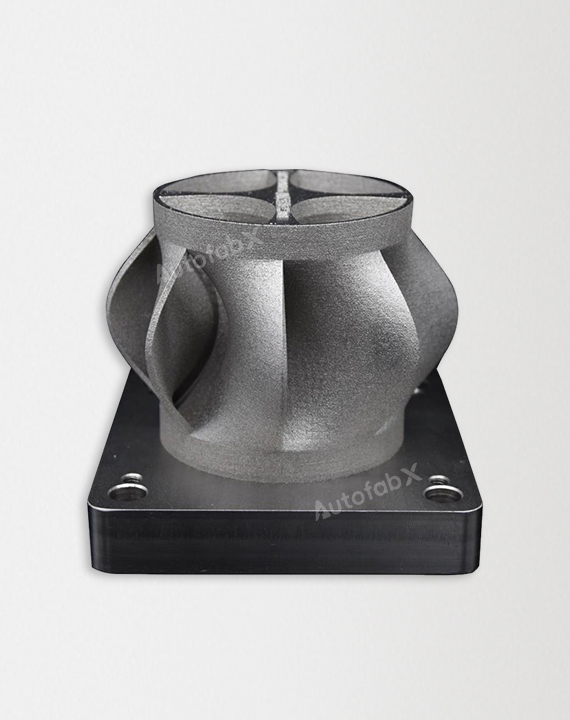
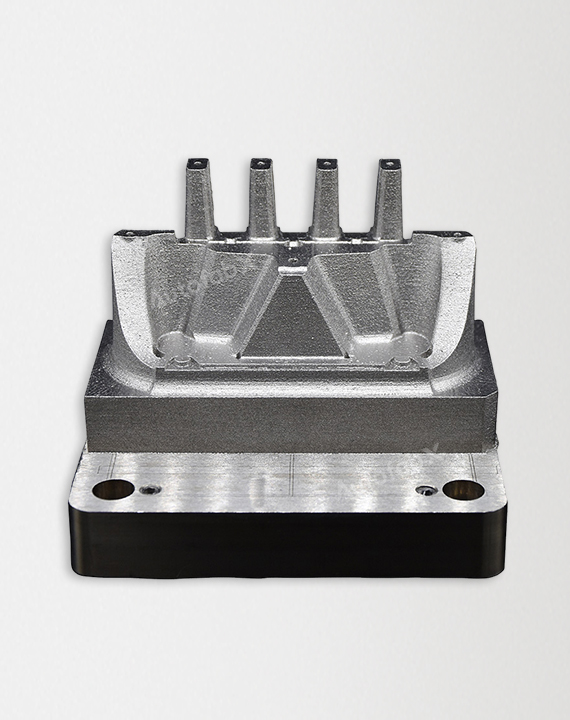
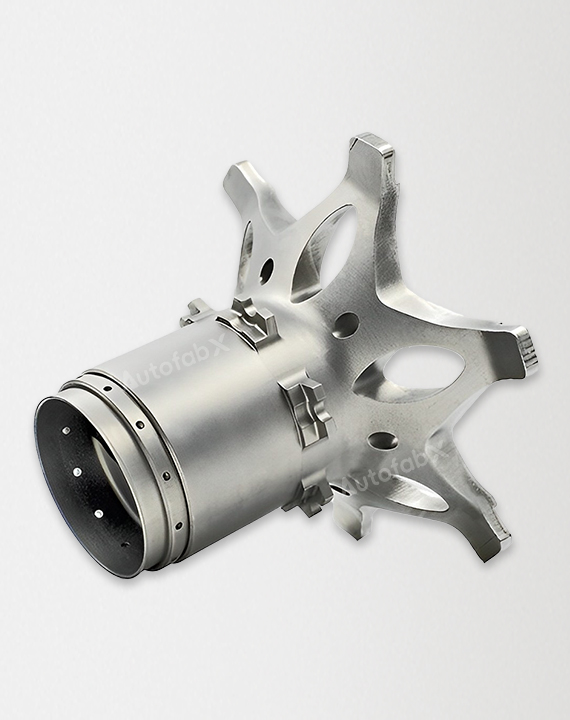
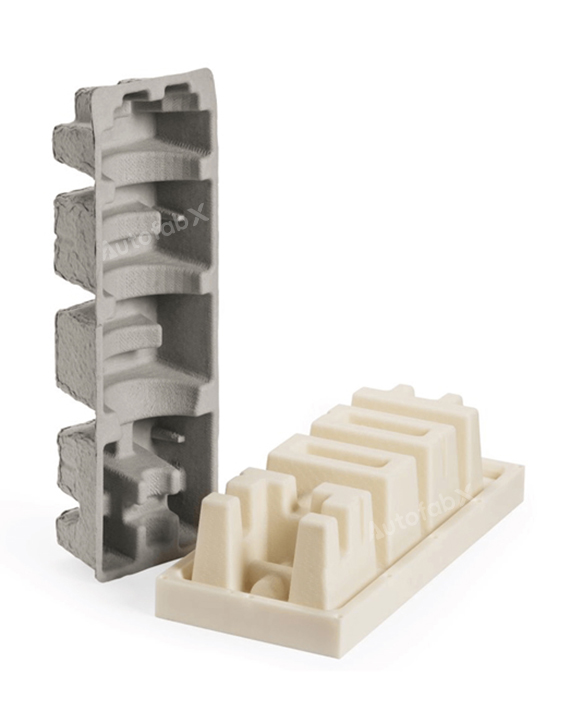
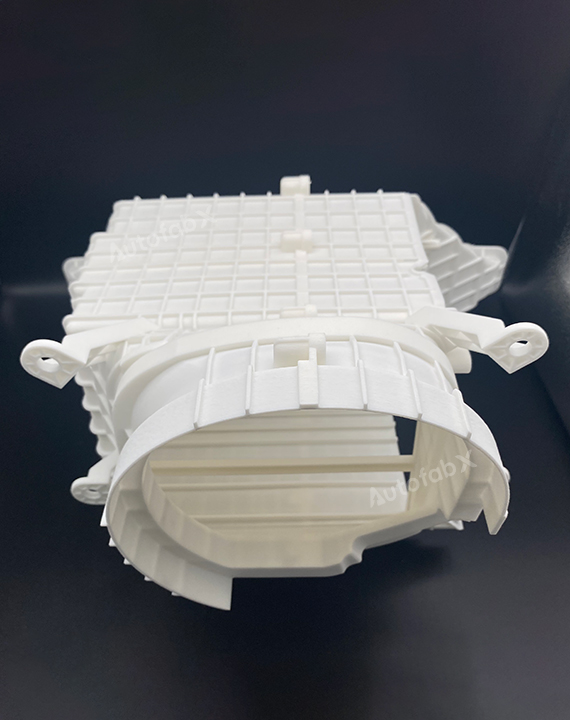
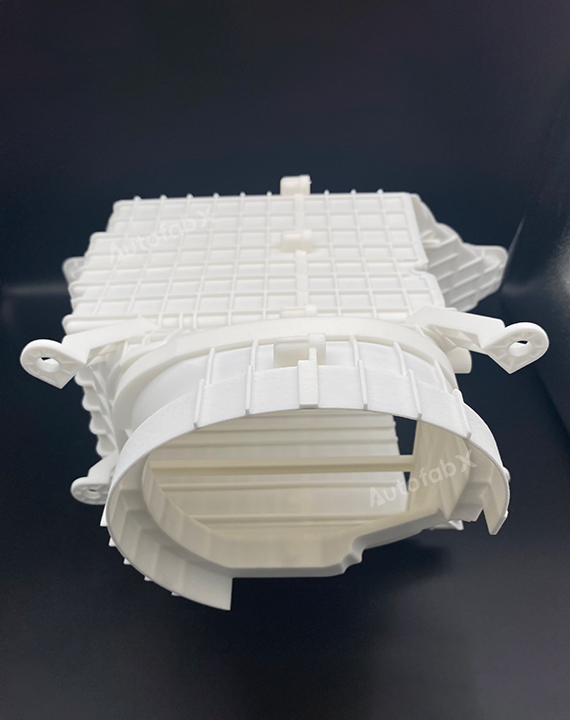
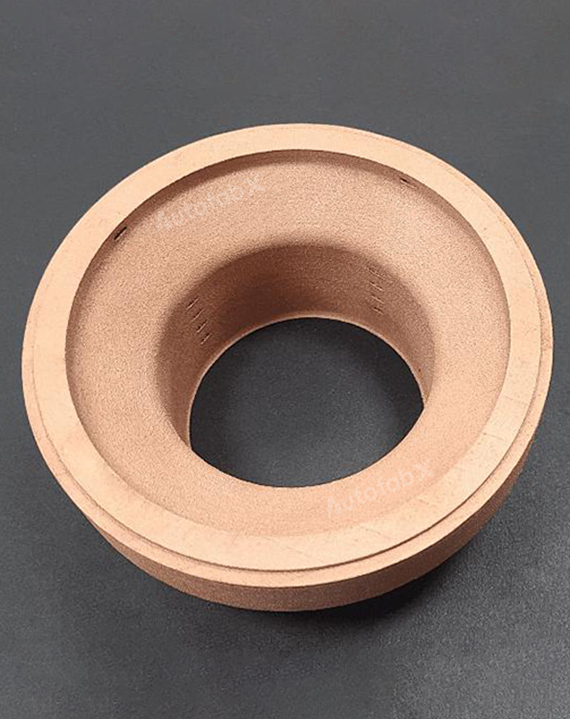
Parts Made by AutofabX