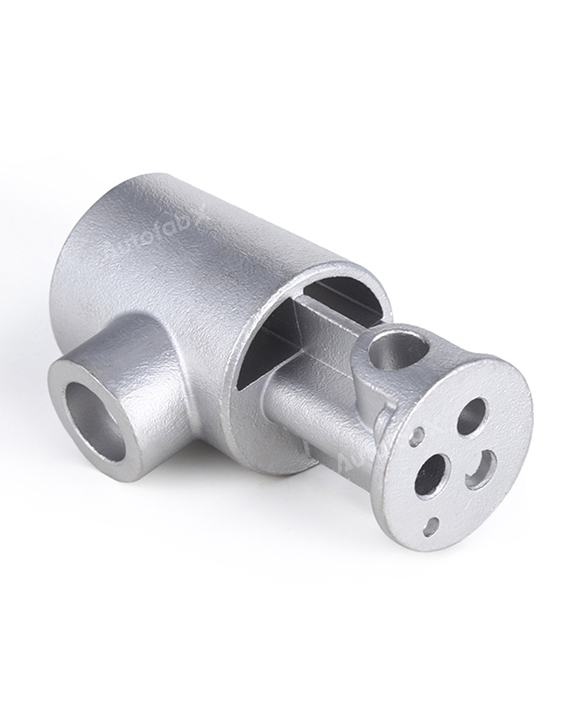
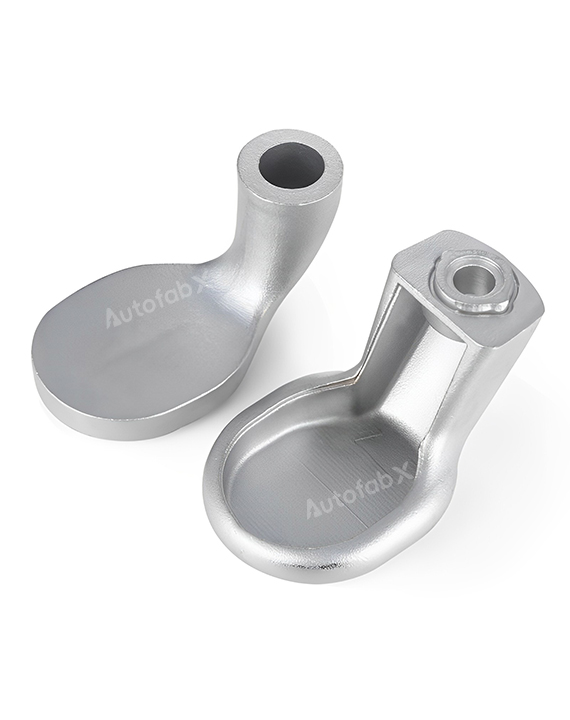
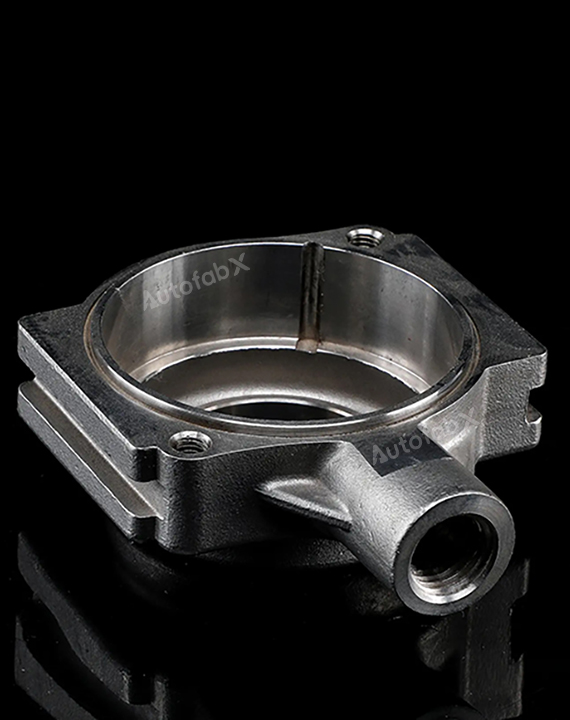
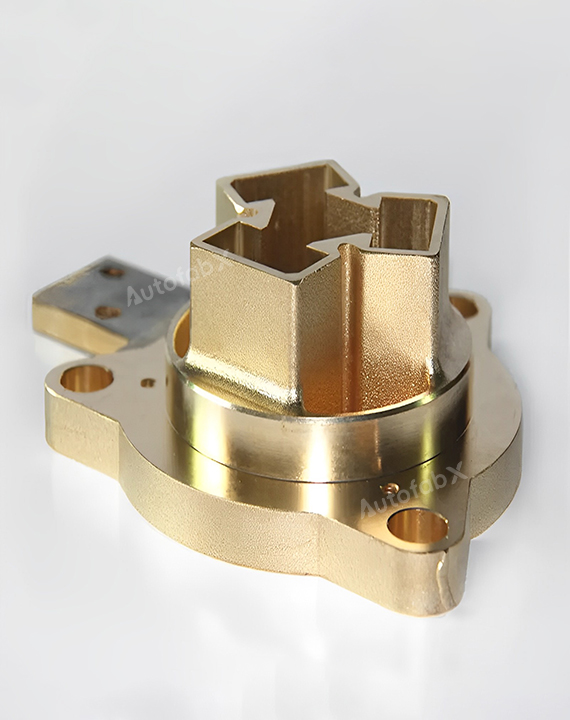
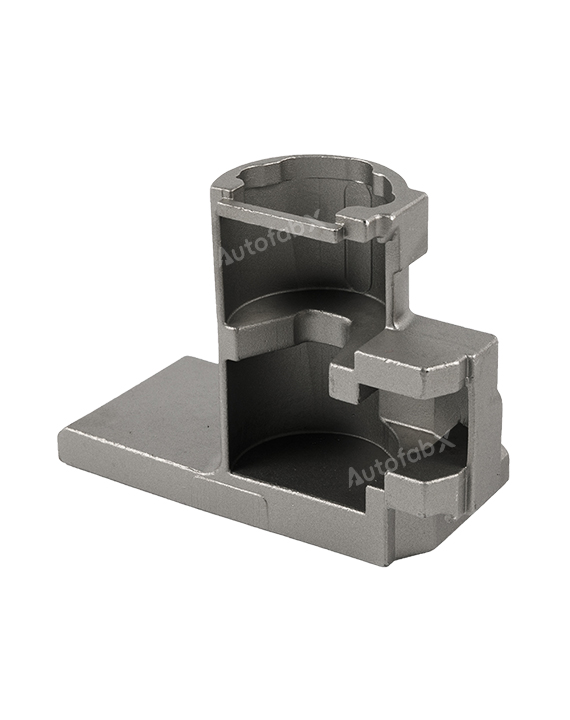
Custom Online Rapid Investment Casting Services
First Order Discount, Quick Delivery, Quality Assurance and Certifications with AutofabX
Start A New Quote
STEP | STP | IGS | DWG | DXF | PDF FilesRapid Investment Casting Materials
RIC Aluminum Alloys
Lightweight and High Strength, Excellent Corrosion Resistance, Superior Machinability
Finishing:
Sand Blasting, Polishing, Powder Coating, Painting, Electrocoating, Shot Blasting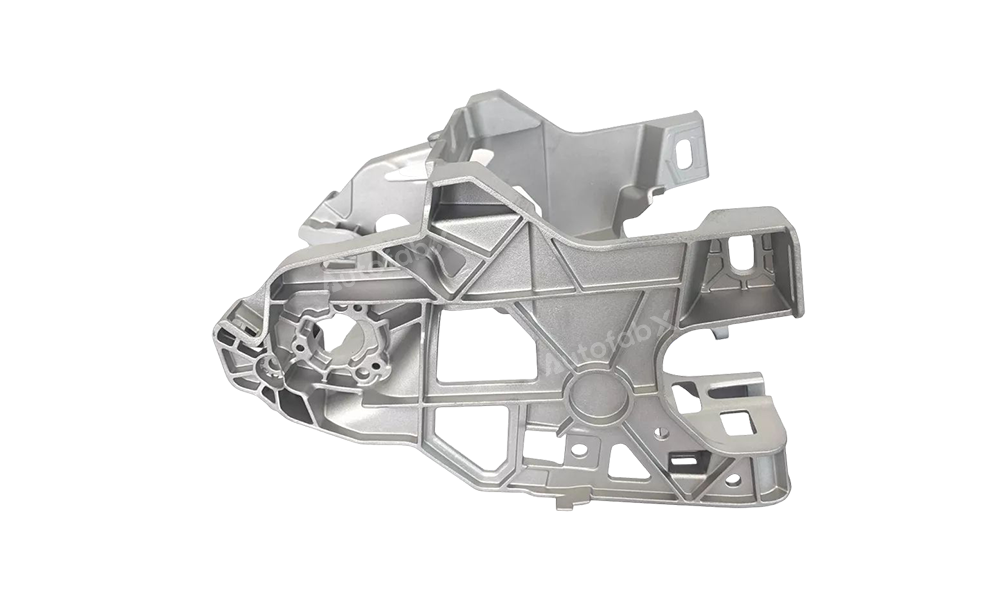
Overview
Rapid Investment Casting is an advanced manufacturing process that combines traditional investment casting with modern rapid prototyping techniques. This method is used to produce complex, high-quality metal parts with a quick turnaround time. The process involves creating a wax or resin pattern, which is then coated with a ceramic shell to form a mold. After the pattern is melted away, molten metal is poured into the mold to create the final part. Rapid Investment Casting is highly suitable for prototyping and low-volume production, offering excellent surface finish, dimensional accuracy, and material versatility.
AutofabX Platform Advantages in Rapid Investment Casting:
Advanced Prototyping Integration: AutofabX leverages state-of-the-art 3D printing technology to produce high-quality wax or resin patterns, ensuring faster and more precise mold creation.
Efficient Production Workflow: The platform integrates automated production scheduling and resource management, allowing for a streamlined workflow from design to finished casting, reducing delays and optimizing lead times.
Customization and Flexibility: AutofabX provides a high level of customization, accommodating unique customer requirements for both design complexity and material selection, ensuring the final product meets exact specifications.
Quality Assurance: AutofabX employs rigorous quality control at each stage of the process, from pattern creation to final casting, ensuring consistent product quality and reducing defects.
Expert Technical Support: The platform offers expert consultation and technical support, helping clients optimize their designs for manufacturability and ensure that the casting process meets their specific needs.
Cost Optimization: By reducing tooling requirements and incorporating rapid prototyping, AutofabX minimizes upfront costs and ensures cost-effectiveness, especially for small to medium production volumes.
Sustainable Practices: AutofabX utilizes efficient material usage and waste reduction practices, contributing to a more sustainable casting process by minimizing waste during both pattern production and metal pouring stages.
These capabilities make AutofabX a leading choice for clients looking for a reliable, high-quality, and cost-effective solution for Rapid Investment Casting projects, especially when quick turnaround and design flexibility are critical.
Process
Rapid Investment Casting Process Steps:
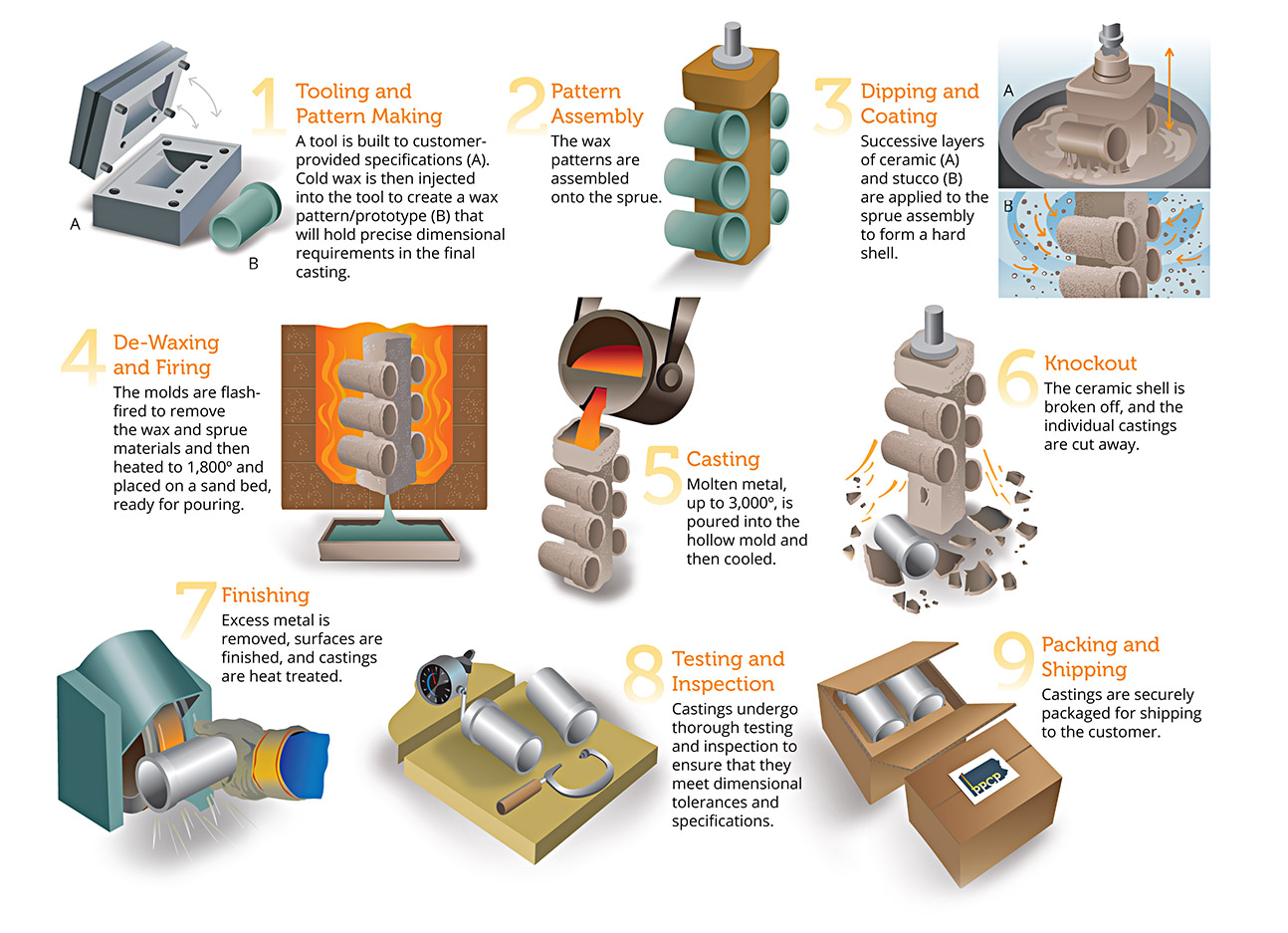
Tooling and Pattern Making: A tool is built to customer specifications, and cold wax is injected into the tool to create a wax pattern that holds precise dimensional requirements.
Pattern Assembly: Wax patterns are assembled onto a sprue.
Dipping and Coating: Successive layers of ceramic and stucco are applied to the sprue assembly to form a hard shell.
De-Waxing and Firing: The molds are flash-fired to remove the wax and sprue materials, then heated and placed on a sand bed, ready for pouring.
Casting: Molten metal is poured into the hollow mold and then cooled.
Knockout: The ceramic shell is broken off, and individual castings are cut away.
Finishing: Excess metal is removed, surfaces are finished, and castings are heat treated.
Testing and Inspection: Castings undergo thorough testing to ensure they meet dimensional tolerances and specifications.
Packing and Shipping: Castings are securely packaged for shipping to the customer.
Rapid Investment Casting is highly suitable for prototyping and low-volume production, offering excellent surface finish, dimensional accuracy, and material versatility.
Equipment Used in Rapid Investment Casting and Leading Brands:
Wax Injection Machines:
Leading Brands: MPI Systems, Westech, Sinto
Pattern Assembly Tools:
Leading Brands: Renfert, KaVo, Heraeus Kulzer
Ceramic Slurry Coating Equipment:
Leading Brands: Ransom & Randolph, Shell-O-Matic, REMET
Autoclaves for De-Waxing:
Leading Brands: Tuttnauer, ASC Process Systems, WSF Industries
Burnout Furnaces:
Leading Brands: Nabertherm, Carbolite Gero, Ipsen
Metal Melting Furnaces:
Leading Brands: Inductotherm, ECM Technologies, OTTO JUNKER
Knockout and Shell Removal Equipment:
Leading Brands: Pangborn, Rosler, Wheelabrator
Finishing and Grinding Machines:
Leading Brands: 3M, Metabo, Dynabrade
Inspection and Testing Equipment:
Leading Brands: Mitutoyo, ZEISS, Nikon Metrology
Analyze
Advantages of Rapid Investment Casting:
Complex Geometries: Capable of producing intricate and detailed components that are difficult to achieve with other casting methods.
High Precision and Quality: Provides excellent dimensional accuracy and a superior surface finish, minimizing the need for post-processing.
Material Versatility: Supports a wide range of metals, including stainless steel, aluminum, and titanium, allowing flexibility in material selection.
Quick Turnaround: Combines rapid prototyping with casting, significantly reducing lead times and enabling faster product iterations.
Cost-Effective for Small Batches: Ideal for prototyping and low-volume production runs, reducing tooling costs compared to traditional casting methods.
Limitations of Rapid Investment Casting:
High Initial Tooling Costs: The initial investment for tooling can be high, making it less suitable for very low-volume production.
Size Limitations: The process is generally limited to small to medium-sized parts due to the nature of the wax pattern and ceramic shell.
Complex Debinding and Sintering: The debinding and sintering processes require careful control to avoid defects and achieve desired quality.
Brittleness of Ceramic Shell: The ceramic shell is fragile, which can lead to breakage during handling, impacting production yield.
Limited Material Selection for Rapid Prototyping: Some metals are difficult to cast using this method, which may limit material choices compared to other casting techniques.
Industry Applications and Case Studies for Rapid Investment Casting:
Aerospace Industry:
Application: Production of turbine blades, structural components, and complex brackets.
Case Study: An aerospace company used Rapid Investment Casting to produce turbine blades with intricate cooling channels, achieving improved fuel efficiency and reduced emissions.
Medical Industry:
Application: Manufacturing of orthopedic implants, surgical instruments, and dental components.
Case Study: A medical device manufacturer employed Rapid Investment Casting to create custom orthopedic implants, resulting in a faster production cycle and precise fit for patients.
Automotive Industry:
Application: Production of exhaust components, turbocharger housings, and lightweight structural parts.
Case Study: An automotive supplier used Rapid Investment Casting to produce complex exhaust system components, which reduced weight and improved engine performance.
Industrial Equipment:
Application: Manufacturing of pumps, valves, and other complex machinery parts.
Case Study: An industrial equipment manufacturer utilized Rapid Investment Casting to create intricate valve bodies, improving flow efficiency and reducing production costs.
Consumer Products:
Application: Production of jewelry, art pieces, and other intricate consumer goods.
Case Study: A jewelry company adopted Rapid Investment Casting to produce highly detailed custom jewelry, allowing for rapid design iterations and customer-specific customization.
Quality Control Standards and Inspection Methods:
Dimensional Inspection:
Tools: Coordinate Measuring Machines (CMM), calipers, and gauges are used to verify dimensional accuracy against design specifications.
Non-Destructive Testing (NDT):
Methods: X-ray inspection and ultrasonic testing are employed to detect internal defects without damaging the part.
Surface Finish Inspection:
Techniques: Visual inspection and surface profilometers are used to ensure the castings meet surface quality requirements.
Mechanical Property Testing:
Tests: Tensile testing, hardness testing, and impact testing are conducted to verify that the casting meets the required mechanical properties.
Material Analysis:
Methods: Spectroscopy and chemical analysis are used to ensure the alloy composition meets the specified requirements.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Rapid Investment Casting:
What types of metals can be used in Rapid Investment Casting?
A wide range of metals, including stainless steel, aluminum, titanium, and cobalt-chrome, can be used in this process.
What is the typical lead time for Rapid Investment Casting?
Lead times can vary, but typically range from 2 to 6 weeks, depending on part complexity and production volume.
Is Rapid Investment Casting suitable for large-scale production?
It is most cost-effective for prototyping and low to medium production volumes. For very large-scale production, other casting methods may be more suitable.
What are the main advantages of Rapid Investment Casting over traditional casting?
The main advantages include quicker lead times, the ability to create complex geometries, and reduced tooling costs for small batches.
How does the quality of Rapid Investment Casting compare to traditional methods?
Rapid Investment Casting offers comparable, if not superior, quality in terms of dimensional accuracy and surface finish, especially for complex parts.
What industries benefit most from Rapid Investment Casting?
Aerospace, medical, automotive, industrial equipment, and consumer products industries benefit greatly from the flexibility and precision of Rapid Investment Casting.
How does AutofabX enhance the Rapid Investment Casting process?
AutofabX integrates advanced 3D printing for pattern making, automates production scheduling, and employs rigorous quality control, ensuring faster lead times and consistent quality.
Are there size limitations for parts produced by Rapid Investment Casting?
Yes, the process is generally more suited to small to medium-sized parts, as the wax patterns and ceramic shells used in the process can be fragile for very large components.
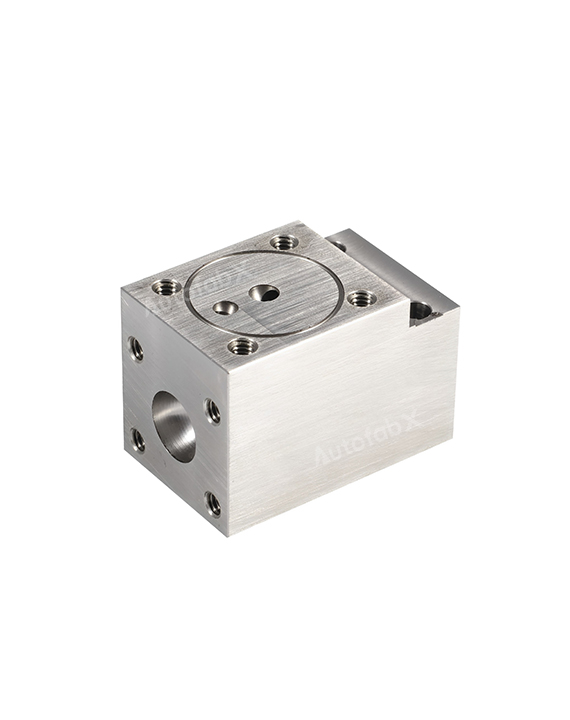
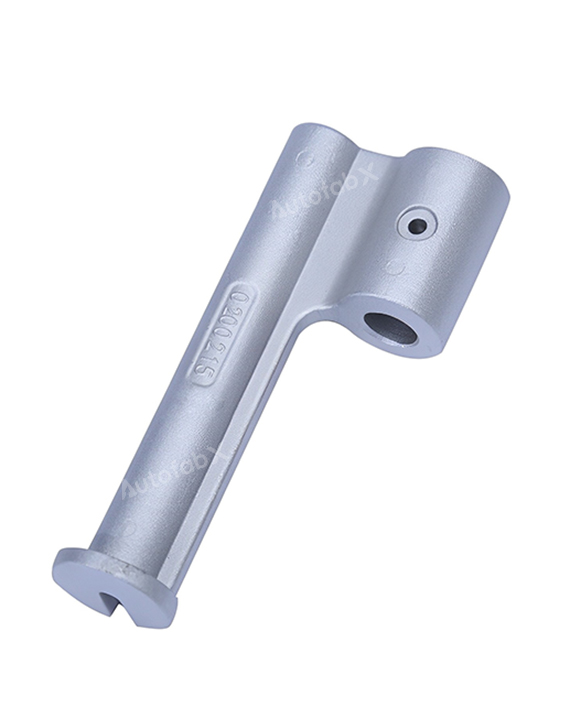
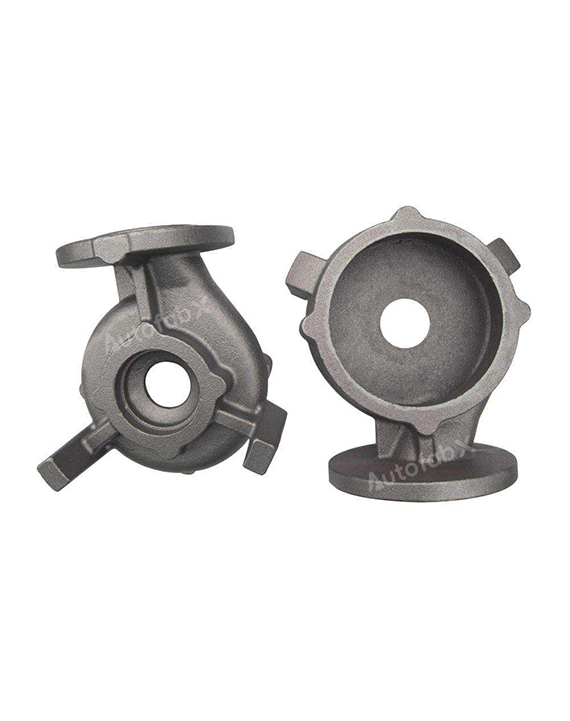
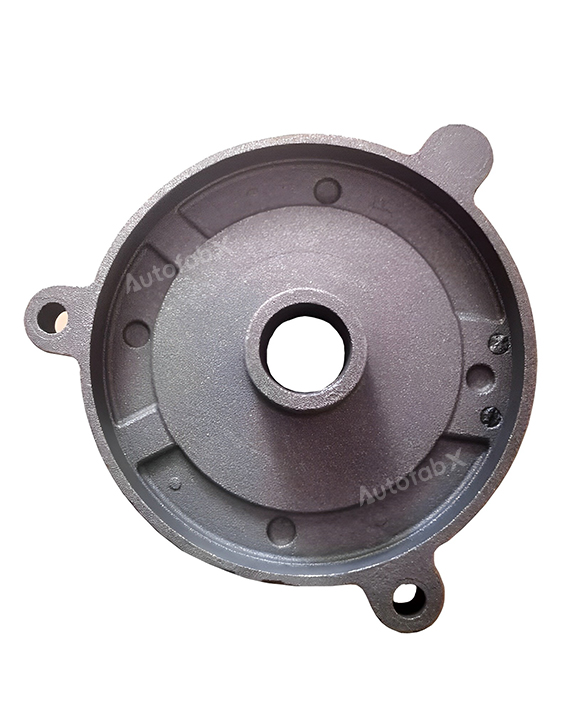
Parts Made by AutofabX