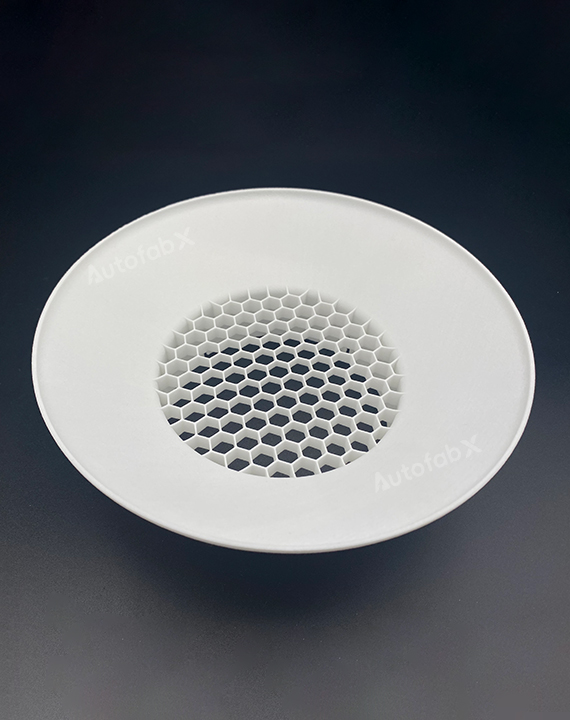
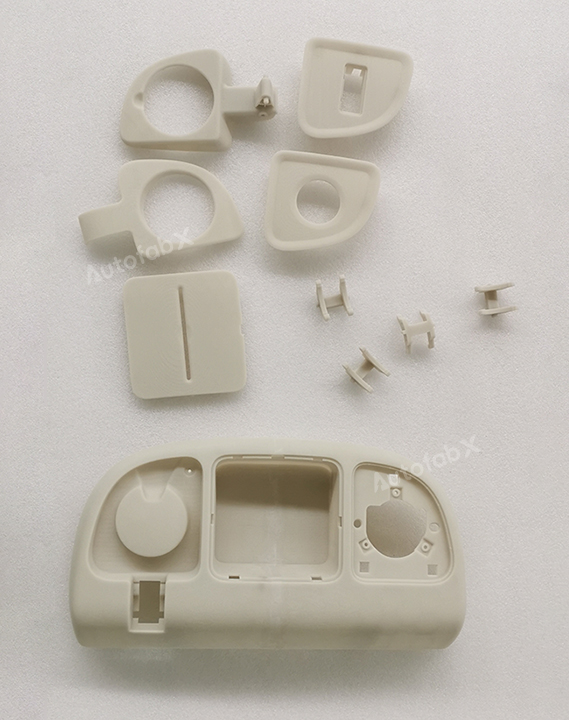
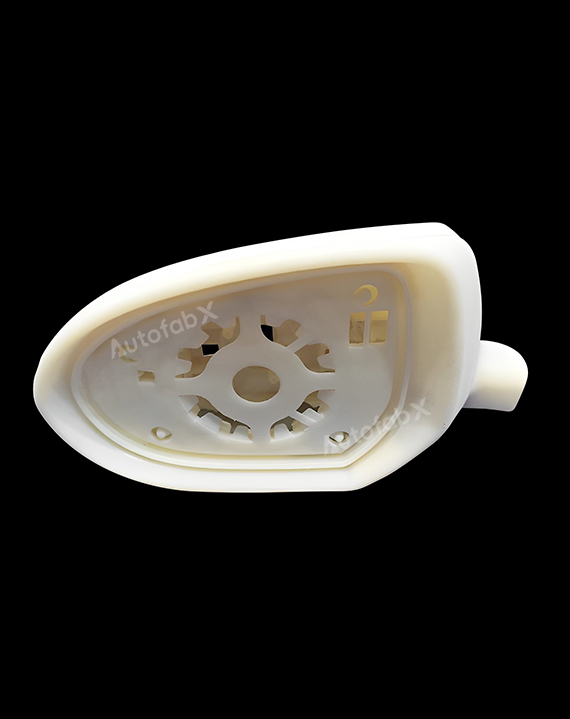
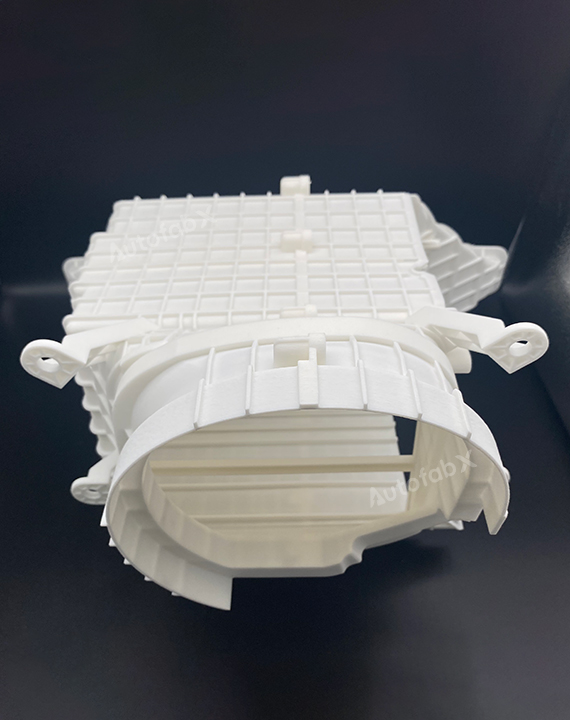
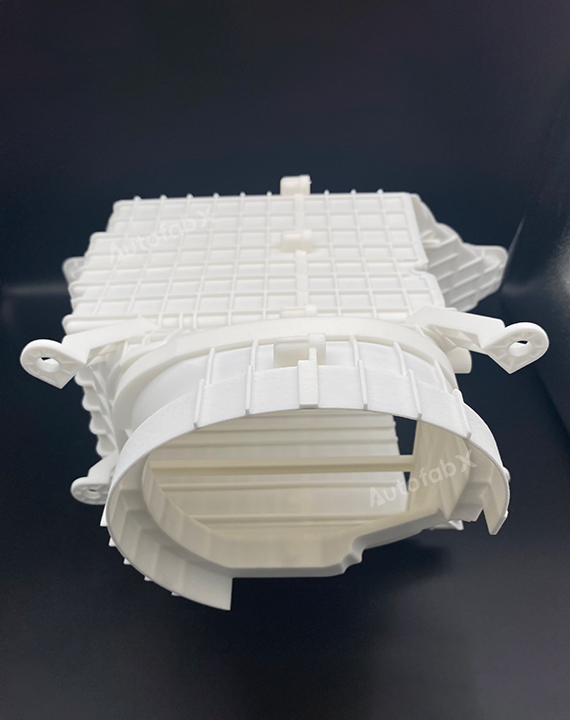
Custom Online Selective Laser Sintering(SLS) Services
Material Versatility, High Precision and Durability, Complex Geometries, Expert Support
Start A New Quote
STEP | STP | IGS | DWG | DXF | PDF FilesSelective Laser Sintering(SLS) Materials
Nylon 11(Black)
Nylon 11(Black) is a high-performance material known for its exceptional impact resistance, excellent toughness, low water absorption, and good oil resistance. These properties make it ideal for demanding applications such as fuel pipelines, retaining rings, snap-fit components, prosthetics, and protective braces, ensuring durability and stability in various environments.
Finishing:
Paint Matte, Sand Blasting, Vapor Smooth, Dye Black
Overview
What is Selective Laser Sintering (SLS)?
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) is an additive manufacturing technology that uses a laser to sinter powdered material, typically nylon or other thermoplastics, layer by layer to form a solid structure. It is known for producing strong, durable parts with complex geometries, making it ideal for both prototyping and end-use production.
Why Choose AutofabX for SLS Services?
AutofabX offers high-quality SLS printing services with several key benefits:
Material Versatility: We offer a wide range of SLS materials, including nylon, glass-filled nylon, and other advanced engineering powders.
High Precision and Durability: Our SLS printers produce parts with excellent accuracy and consistent mechanical properties, suitable for functional prototypes and end-use parts.
Complex Geometries: SLS allows for the production of complex, interlocking parts without the need for support structures, enabling greater design freedom.
Expert Support: Our team offers design optimization for additive manufacturing, ensuring the best possible results for your SLS projects.
How Selective Laser Sintering Works
Design: The process begins with a 3D CAD model, which is prepared in slicing software to create a layer-by-layer plan.
Powder Layering: A thin layer of powder material is spread across the build platform.
Laser Sintering: A high-powered laser selectively fuses the powder particles by scanning over the surface, following the cross-sectional pattern of the part.
Layering: The build platform lowers, and a new layer of powder is spread. The laser fuses this layer with the previous one, and the process continues until the part is complete.
Cooling and Post-Processing: Once the build is complete, the parts are allowed to cool before excess powder is removed. Post-processing may include bead blasting or dyeing.
Main Equipment for SLS Printing and Popular Brands
3D Systems ProX SLS 6100: Known for its high precision and ability to produce strong, functional parts.
EOS Formiga P 110: Offers excellent reliability and is widely used for both prototyping and production of industrial-grade parts.
Advantages and Limitations of SLS Printing
Advantages:
Complex Geometries: SLS can produce parts with complex geometries, including internal features and interlocking parts, without the need for support structures.
Functional Materials: SLS materials, such as nylon, provide excellent mechanical properties, making the parts suitable for functional testing and end-use applications.
Batch Production: SLS is well-suited for batch production, allowing multiple parts to be printed simultaneously.
No Support Structures: Parts are printed within a powder bed, which provides natural support, eliminating the need for additional support structures.
Limitations:
Surface Finish: SLS parts may have a rough surface finish and require additional post-processing for a smooth appearance.
Porosity: Parts produced via SLS can be porous, and additional infiltration may be needed to improve their density and mechanical properties.
Cooling Time: The cooling process can take a significant amount of time, which may impact overall production speed.
Industry Applications and Case Studies for SLS Printing
Aerospace Industry:
Application: Production of lightweight, durable components for aircraft.
Case Study: An aerospace manufacturer used SLS to create complex ducting components, reducing weight while maintaining strength and durability.
Medical Industry:
Application: Production of medical devices, prosthetics, and surgical guides.
Case Study: A medical device company utilized SLS to produce custom prosthetic devices, providing a perfect fit for individual patients.
Consumer Goods:
Application: Manufacturing of customized products and prototypes.
Case Study: A consumer goods company used SLS to create ergonomic handles for a new product line, allowing for rapid prototyping and user testing.
Quality Control Standards and Inspection Methods for SLS Printing
Dimensional Inspection
Tools: Calipers and Coordinate Measuring Machines (CMM) are used to verify the dimensions of printed parts.
Density and Porosity Testing
Methods: Density testing is performed to assess the level of porosity and determine if additional infiltration is needed.
Mechanical Property Testing
Methods: Tensile, compression, and impact tests are conducted to ensure the printed parts meet the required mechanical standards.
SLS Printing Design Guidance Table
| Design Aspect | Recommendation |
| Minimum Wall Thickness | 1.0 mm |
| Minimum Feature Size | 0.8 mm |
| Overhangs | Self-supporting |
| Tolerance | ±0.3 mm |
| Layer Height | 100-120 microns |
SLS Printing Precision Table
| Printing Process | Typical Tolerance |
| Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) | ±0.3 mm |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about SLS Printing
What materials can be used in SLS printing?
SLS can use a variety of powdered materials, including nylon (PA12), glass-filled nylon, and TPU, suitable for functional parts and prototypes.
Is SLS printing suitable for functional parts?
Yes, SLS produces parts with excellent mechanical properties, making it ideal for functional prototypes and end-use applications.
What industries benefit from SLS printing?
Industries such as aerospace, medical, and consumer goods benefit from the precision, material properties, and design freedom offered by SLS printing.
How accurate is SLS printing?
SLS printing can achieve tolerances of ±0.3 mm, which is suitable for many functional and prototyping applications.
What post-processing is required for SLS-printed parts?
Post-processing may include bead blasting, dyeing, or infiltration to improve surface finish and mechanical properties.
Can SLS print flexible parts?
Yes, SLS can print with TPU, a flexible material, which is useful for applications requiring elasticity.
How strong are SLS-printed parts?
SLS-printed parts are strong and durable, with mechanical properties that make them suitable for functional use.
Parts Made by AutofabX